Hospitalization expenses of coronary heart disease inpatients in China: evidence from two hospitals in Ningxia Hui autonomous region
- PMID: 38756881
- PMCID: PMC11096531
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1266456
Hospitalization expenses of coronary heart disease inpatients in China: evidence from two hospitals in Ningxia Hui autonomous region
Abstract
Aim: The increasing morbidity from coronary health disease (CHD) has imposed a significant social and economic burden in China. We analyzed the factors affecting hospitalization expenses of CHD patients.
Design: From 2012 to 2018, data on 16,726 CHD patients were collected from the hospital information system in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region.
Methods: A multiple ordered logistic regression model was used to analyze the factors affecting hospitalization expenses.
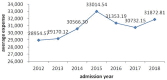
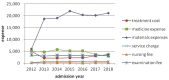
Results: The average hospitalization expense was RMB30998.26 ± 29890.03. Hospital materials expenses accounted for roughly 60% of total hospitalization costs. The older adult, patients who were male, in critical health status, with longer hospital stays, unemployed, using antibiotics and undergoing an operation without incision had significantly raised hospital expenses, while those with fewer complications, no operations and self-paying for health care had reduced hospitalization costs (p < 0.05). The length of hospital stay played a partial mediator role (p < 0.05).
Public contribution: Controlling the increase of medical materials costs and preventing over-consumption of hospital services by insured patients are recommended.
Keywords: coronary heart disease; cost; health policy; hospitalization expenses; inpatient.
Copyright © 2024 Xu, Liu, Wang and Nicholas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of hospitalization expenditures and influencing factors for inpatients with coronary heart disease in a tier-3 hospital in Xi'an, China: A retrospective study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Dec;96(51):e9341. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009341. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 29390516 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Associated With Hospitalization Costs of Coronary Heart Disease in Township Hospitals in Rural China.Inquiry. 2019 Jan-Dec;56:46958019886958. doi: 10.1177/0046958019886958. Inquiry. 2019. PMID: 31701787 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Economic Insights into Parkinson's Disease Hospitalization: A Comprehensive Study of 19,719 Inpatient Cases in Hubei Province, China.Neuroepidemiology. 2024;58(4):237-246. doi: 10.1159/000536525. Epub 2024 Jan 30. Neuroepidemiology. 2024. PMID: 38290491 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of hospitalization expenses and influencing factors for elderly cancer patients in a tertiary hospital in Dalian, China: a five‑year retrospective study.BMC Cancer. 2024 Jul 18;24(1):864. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12635-6. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39026195 Free PMC article.
-
Mental health inpatient treatment expenditure trends in China, 2005-2012: evidence from Shandong.J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2014 Dec;17(4):173-82. J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2014. PMID: 25599281
References
-
- National Health Commission of China . The statistical bulletin on health development in China in 2008 (2009). Available at: http://www.gov.cn/gzdt/2009-04/29/content_1299547.htm (Accessed April 29, 2009)
-
- National Health Commission of China . The statistical bulletin on health development in China in 2018 (2019). Available at: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/guihuaxxs/s10748/201905/9b8d52727cf346049de8acce25... (Accessed May 22, 2019)
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources