Association of IL‑6 and MMP‑3 gene polymorphisms with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A systematic review and meta‑analysis
- PMID: 38756907
- PMCID: PMC11097290
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2024.12555
Association of IL‑6 and MMP‑3 gene polymorphisms with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A systematic review and meta‑analysis
Abstract
The pathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) remains unclear. It has been found that interleukin-6 (IL-6) rs1800795 locus and matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) rs3025058 locus gene polymorphisms may be associated with AIS susceptibility, which has been controversial and needs to be further confirmed by updated meta-analysis. The aim of the present study was to investigate the association of MMP-3 rs3025058 and IL-6 rs1800795 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with susceptibility to AIS. All relevant articles that met the criteria were retrieved and included, and the publication dates were limited from January 2005 to December 2023. The allele frequencies and different genotype frequencies of IL-6 rs1800795 and MMP-3 rs3025058 loci in each study were extracted and statistically analyzed by ReviewManager 5.4 software, and the odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (95% CI) of different genetic models were calculated. The results of the meta-analysis showed that there was no significant association between the gene polymorphism of IL-6 rs1800795 locus and the pathogenesis of AIS. The allele 5A and genotype 5A5A of MMP-3 rs3025058 SNP were associated with AIS susceptibility (5A vs. 6A, OR=1.18; 95% CI, 1.04-1.33; 5A5A vs. 6A6A, OR=1.65; 95% CI, 1.23-2.21; and 5A5A vs. 5A6A + 6A6A, OR=1.54; 95% CI, 1.19-1.99). Results of subgroup analysis revealed that the allele 5A and genotype 5A5A of MMP-3 rs3025058 SNP were associated with AIS susceptibility in the Caucasian population, and the susceptibility of AIS was associated with the genotype 5A5A of MMP-3 rs3025058 SNP in an Asian population. There was no significant association between the gene polymorphism of IL-6 rs1800795 locus and the pathogenesis of AIS, while the allele 5A of MMP-3 rs3025058 locus was associated with the susceptibility to AIS, especially in the Caucasian population.
Keywords: IL-6; MMP-3; adolescent idiopathic scoliosis; meta-analysis; single nucleotide polymorphism.
Copyright: © 2024 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
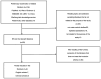








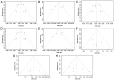
References
-
- Kuznia AL, Hernandez AK, Lee LU. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Common questions and answers. Am Fam Physician. 2020;101:19–23. - PubMed
-
- Lin J, Wong CKH, Cheung JPY, Cheung PWH, Luo N. Psychometric performance of proxy-reported EQ-5D youth version 5-level (EQ-5D-Y-5L) in comparison with three-level (EQ-5D-Y-3L) in children and adolescents with scoliosis. Eur J Health Econ. 2022;23:1383–1395. doi: 10.1007/s10198-022-01435-z. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
