Cold Air Plasma Inhibiting Tumor-Like Biological Behavior of Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synovial Cells via G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest
- PMID: 38756916
- PMCID: PMC11096841
- DOI: 10.2147/OARRR.S438536
Cold Air Plasma Inhibiting Tumor-Like Biological Behavior of Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synovial Cells via G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest
Abstract
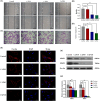
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synovial cells (RA-FLS) have become the core effector cells for the progression of rheumatoid arthritis due to their "tumor-like cell" characteristics, such as being able to break free from growth restrictions caused by contact inhibition, promoting angiogenesis, invading surrounding tissues, and leading to uncontrolled synovial growth. In recent years, cold air plasma (CAP) has been widely recognized for its clear anticancer effect. Inspired by this, this study investigated the inhibitory effect of CAP on the tumor-like biological behavior of RA-FLS through in vitro experiments.
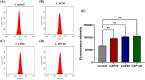
Methods: Treatment of RA-FLS with CAP at different time doses (0s, 30s, 60s, 120s). 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU) proliferation assay was used to determine the cell viability. Analysis of cell migration and invasion was performed by wound-healing assay, transwell assay and immunofluorescent staining for f-actin, respectively. Flow cytometry technique was used for analysis of cell cycle and determination of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Hoechst staining was used for analysis of cell apoptosis. Protein expression was analyzed by Western blot analysis.
Results: Molecular and cellular level mechanisms have revealed that CAP blocks RA-FLS in the G2/M phase by increasing intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to increased apoptosis and significantly reduced migration and invasion ability of RA-FLS.
Conclusion: Overall, CAP has significant anti proliferative, migratory, and invasive effects on RA-FLS. This study reveals a new targeted treatment strategy for RA.
Keywords: apoptosis; cold air plasma; migration; proliferation; rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synovial cells.
© 2024 Ni et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

