Diagnosing and Treating Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis and Adult-Onset Still's Disease as Part of the Still's Disease Continuum
- PMID: 38756937
- PMCID: PMC11094444
- DOI: 10.31138/mjr.290323.dat
Diagnosing and Treating Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis and Adult-Onset Still's Disease as Part of the Still's Disease Continuum
Abstract
Aim: We have summarised the existing evidence supporting the concept that systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA) and adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD) are part of the same Still's disease spectrum.
Methods: A PubMed/Embase database search was conducted using specific search strings and free text words to screen for relevant articles. The search was limited to studies in humans, published up to June 2023, in English-language.
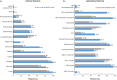
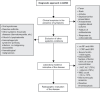
Summary: sJIA and AOSD are rare autoinflammatory disorders that have similar pathophysiological and clinical features. The clinical presentations of sJIA and AOSD are highly variable, with differential diagnoses that include a broad range of malignancies, infectious diseases, and autoimmune disorders, which contribute to delays in diagnosis. Several sets of classification exist to help diagnose patients in clinical practice; the International League of Associations for Rheumatology criteria for sJIA and the Yamaguchi and Fautrel criteria for AOSD are the most-used criteria. The therapeutic strategy for Still's disease aims to relieve signs and symptoms, prevent irreversible joint damage and potentially life-threatening complications, and avoid deleterious side effects of treatment. Recently, targeted therapies such as interleukin (IL)-1 and IL-6 inhibitors have become available for the treatment of sJIA and AOSD. While these biologics were originally largely reserved for patients in whom non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids and conventional synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs had failed, they are increasingly used earlier in the treatment paradigm. Among IL-1 inhibitors, canakinumab is the only biologic approved in the US for the treatment of both sJIA and AOSD.
Keywords: adult-onset Still’s disease; autoinflammatory disease; biologics; macrophage activation syndrome; systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
© 2024 The Mediterranean Journal of Rheumatology (MJR).
Conflict of interest statement
Apostolos Kontzias: consultant for Kiniksa, Sobi and Novartis; Olga Petryna: consultant for Novartis and Pfizer; Priscila Nakasato: None; Petros Efthimiou: Consultant for Novartis, Kiniksa, Sanofi, and Pfizer.
Figures
References
-
- Jamilloux Y, Gerfaud-Valentin M, Martinon F, Belot A, Henry T, Seve P. Pathogenesis of adult-onset Still’s disease: new insights from the juvenile counterpart. Immunol Res 2015;61(1–2):53–62. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
