Coumarin Glycosides Reverse Enterococci-Facilitated Enteric Infections
- PMID: 38756989
- PMCID: PMC11096794
- DOI: 10.34133/research.0374
Coumarin Glycosides Reverse Enterococci-Facilitated Enteric Infections
Abstract
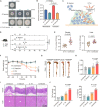
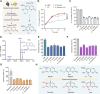
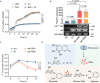
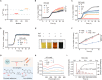
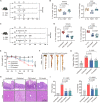
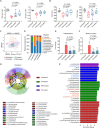
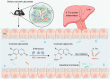
Commensal enterococci with pathogenic potential often facilitate the growth of diverse pathogens, thereby exacerbating infections. However, there are few effective therapeutic strategies to prevent and intervene in enterococci-mediated polymicrobial infections. Here, we find that enterococci at high density drive the expansion and pathogenicity of enteric Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium (S. Tm). Subsequently, we show that the driving role of enterococci in such infections is counteracted by dietary coumarin glycosides in vivo. Enterococci, which are tolerant of iron-deficient environments, produce β-glucosidases to hydrolyze coumarin glycosides into bioactive aglycones, inhibiting S. Tm growth and ameliorating the severity of S. Tm-induced symptoms by inducing iron limitation. Overall, we demonstrate that coumarin glycosides as a common diet effectively reverse enterococci-facilitated enteric infections, providing an alternative intervention to combat polymicrobial infections.
Copyright © 2024 Wenjiao Xu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Zitvogel L, Kroemer G. Immunostimulatory gut bacteria. Science. 2019;366(6469):1077–1078. - PubMed
-
- Freedberg DE, Zhou MJ, Cohen ME, Annavajhala MK, Khan S, Moscoso DI, Brooks C, Whittier S, Chong DH, Uhlemann AC, et al. . Pathogen colonization of the gastrointestinal microbiome at intensive care unit admission and risk for subsequent death or infection. Intensive Care Med. 2018;44(8):1203–1211. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xu W, Fang Y, Zhu K. Enterococci facilitate polymicrobial infections. Trends Microbiol. 2024;32(2):162–177. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

