TLR4 knockdown by miRNA-140-5p improves tendinopathy: an in vitro study
- PMID: 38757029
- PMCID: PMC11094843
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2020.93216
TLR4 knockdown by miRNA-140-5p improves tendinopathy: an in vitro study
Abstract
Introduction: The purpose of this study was to determine whether TLR4 knockdown induced by miRNA-140-5p improves tendinopathy in an in vitro experiment.
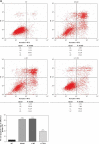
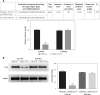
Material and methods: Extraction of tendon-derived stem cells (TDSCs) from SD rats was performed using TGF-β1 to develop a tendinopathy cell model. In the first step, we knocked down TLR4 by si-TLR4 to investigate TLR4 in tendinopathy development, and the next we used miRNA-140-5p to investigate miRNA-140-5p in tendinopathy development. The inflammatory factors and Hyp concentration were evaluated by ELISA assay; the cell viability was measured by MTT assay; the cell apoptosis was evaluated by TUNEL and/or flow cytometry. The relative mRNA was measured by RT-qPCR assay; the relative proteins expression was evaluated by cellular immunofluorescence and/or WB assay. The correlation between miRNA-140-5p and TLR4 was analyzed by Luciferase reporter assay.
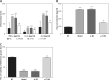
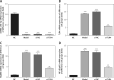
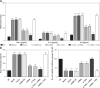
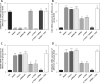
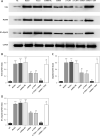
Results: With miRNA-140-5p overexpression or TLR4 knockdown, the cell viability was significantly increased with cell apoptosis depressing compared with the Model group (p < 0.05, respectively). Meanwhile, the inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 and Hyp concentration were significantly improved (p < 0.05, respectively), whereas the TLR4, MyD88 and NF-κB(p65) protein expression levels were significantly depressed with TLR4 knockdown by si-TLR4 or miRNA-140-5p which target TLR4.
Conclusions: The present results showed that TLR4 knockdown induced by miRNA-140-5p or si-TLR4 improved tendinopathy in an in vitro cell experiment.
Keywords: MyD88; NF-κB(p65); TLR4; miRNA-140-5p; tendinopathy.
Copyright: © 2020 Termedia & Banach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Standard Puerarin Prevents Diabetic Renal Damage by Inhibiting miRNA-140-5p Expression.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020 Oct 23;13:3947-3958. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S273952. eCollection 2020. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020. PMID: 33122931 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of Tripterygium glycoside on IL-1β-induced inflammation and apoptosis of rat chondrocytes via microRNA-216a-5p/TLR4/NF-κB axis.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2023 Feb;45(1):61-72. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2022.2115924. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2023. PMID: 36052873
-
[miR-515-5p targeting Toll-like receptor 4 regulates myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88/nuclear factor-kappa B pathway to inhibit apoptosis and inflammatory response of osteoarthritis chondrocytes].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Mar 15;38(3):315-323. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202312091. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38500425 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Dandelion sterol improves diabetes mellitus-induced renal injury in in vitro and in vivo study.Food Sci Nutr. 2021 Jul 28;9(9):5183-5197. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2491. eCollection 2021 Sep. Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34532027 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of FTO alleviates osteoarthritis by regulating the processing of miR-515-5p and the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB axis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Jan;114:109524. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109524. Epub 2022 Dec 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36538851
Cited by
-
Advancements in Therapeutic Approaches for Degenerative Tendinopathy: Evaluating Efficacy and Challenges.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 4;25(21):11846. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111846. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519397 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Snedeker JG, Foolen J. Tendon injury and repair – a perspective on the basic mechanisms of tendon disease and future clinical therapy. Acta Biomater 2017; 63: 18-36. - PubMed
-
- Ackermann PW, Hart DA. General overview and summary of concepts regarding tendon disease topics addressed related to metabolic disorders. Adv Exp Med Biol 2016; 920: 293-8. - PubMed
-
- Schwellnus MP, Swanevelder S, Jordaan E, Derman W, Van Rensburg DCJ. Underlying chronic disease, medication use, history of running injuries and being a more experienced runner are independent factors associated with exercise-associated muscle cramping: a cross-sectional study in 15778 distance runners. Clin J Sport Med 2018; 28: 289-98. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
