Rheumatoid factor titers, but not Fc fragments, may be strongly associated with drug survival of anti-TNF agents in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 38757098
- PMCID: PMC11095329
- DOI: 10.14744/nci.2023.01643
Rheumatoid factor titers, but not Fc fragments, may be strongly associated with drug survival of anti-TNF agents in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of both the Fc fragment in tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors and rheumatoid factor (RF) titers on treatment survival, disease activity, and laboratory parameters in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, patients with RA who had started any anti-TNF therapy between January 2017 and March 2020 and who had stayed on this treatment for at least six months were included. The data of the patients were compared separately according to continuation or discontinuation of treatment and the presence or absence of Fc portion in the structure of anti-TNFs. Patients who were taking certolizumab pegol (CZP) without the Fc fragment were placed in the "without Fc group" (wo/Fc), while patients who were taking other drugs (adalimumab, etanercept, golimumab, and infliximab) were placed in the "with Fc group" (w/Fc).
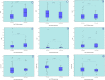
Results: Among the 221 RA patients whose data were available, 52 patients met the inclusion criteria and were included in the study. There was a significant difference in the DAS28-CRP score between wo/Fc group and w/Fc group in the third month of treatment (p=0.012). However, this difference did not persist at the sixth month of treatment (p=0.384). According to the cox-regression results, RF titers were determined to have a significant impact on the drug survival of anti-TNF agents when adjustments were made for the effects of other candidate predictors (Hazard ratio: 1.007 (1.002-1.012), p=0.009).
Conclusion: Our results suggest that compared to the Fc fragment, RF titers were the more important risk factor in survival of anti-TNF drugs.
Keywords: Fc fragments; TNF inhibitors; rheumatoid arthritis; rheumatoid factor; treatment.
© Copyright 2024 by Istanbul Provincial Directorate of Health.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential efficacy of TNF inhibitors with or without the immunoglobulin fragment crystallizable (Fc) portion in rheumatoid arthritis: the ANSWER cohort study.Rheumatol Int. 2022 Jul;42(7):1227-1234. doi: 10.1007/s00296-021-05086-w. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Rheumatol Int. 2022. PMID: 35266034
-
Down-titration and discontinuation strategies of tumour necrosis factor-blocking agents for rheumatoid arthritis in patients with low disease activity.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 May 24;5(5):CD010455. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010455.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31125448 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-utility analysis of certolizumab pegol in combination with methotrexate in patients with moderate-to-severe active rheumatoid arthritis in Greece.Rheumatol Int. 2017 Sep;37(9):1441-1452. doi: 10.1007/s00296-017-3736-z. Epub 2017 May 18. Rheumatol Int. 2017. PMID: 28523420
-
Which factors influence radiographic progression during treatment with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in clinical practice? Results from 930 patients with rheumatoid arthritis in the nationwide Danish DANBIO registry.J Rheumatol. 2014 Dec;41(12):2352-60. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.131299. Epub 2014 Oct 1. J Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 25274894
-
Comparison of certolizumab pegol with other anticytokine agents for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a multiple-treatment Bayesian metaanalysis.J Rheumatol. 2011 May;38(5):835-45. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.100665. Epub 2011 Jan 15. J Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21239748
References
-
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Koeller M, Weisman MH, Emery P. New therapies for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2007;370:1861–74. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Steiner G. Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2:473–88. - PubMed
-
- Littlejohn EA, Monrad SU. Early diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Prim Care. 2018;45:237–55. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
