Pycnogenol® French maritime pine bark extract in randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled human clinical studies
- PMID: 38757130
- PMCID: PMC11096518
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1389374
Pycnogenol® French maritime pine bark extract in randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled human clinical studies
Abstract
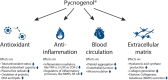
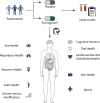
Pycnogenol® French maritime pine bark extract is a well-known and thoroughly studied patented extract from the bark of Pinus pinaster Ait. ssp. Atlantica. In 39 randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled (RDP) human clinical trials including 2,009 subjects, Pycnogenol® French maritime pine bark extract supplementation for two weeks to six months has been shown to beneficially affect cardiovascular health, chronic venous insufficiency, cognition, joint health, skin health, eye health, women's health, respiratory health and allergies, oral health and sports performance. The mechanisms of action that can explain the respective effects on different conditions in the human body are discussed as well. As investigated in several in vitro, in vivo and in clinical studies, Pycnogenol® French maritime pine bark extract showed antioxidative effects, anti-inflammatory abilities, beneficial effects on endothelial function and reinforcing effects on the extracellular matrix. The present review aims to give a comprehensive overview of currently available "gold standard" RDP trials of Pycnogenol®'s benefits across various health domains compared to placebo. In addition, some of the processes on which the presented effects of Pycnogenol® French maritime pine bark extract are based will be elucidated and discussed. This broad overview of RDP studies on Pycnogenol® in different health domains can be used as a basis for further research on applications and mechanisms of this unique French maritime pine bark extract.
Keywords: Pycnogenol®; anti-inflammatory; antioxidant; cardiovascular; double-blind; endothelial health; pine bark extract; placebo-controlled.
Copyright © 2024 Weichmann and Rohdewald.
Conflict of interest statement
FW was an employee of Horphag Research. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Karaçelik AA, Şeker ME, Karaköse M. Determination of antioxidant activity of different extracts from bark of Pinus spp. grown in Giresun (Turkey) province – phenolic analysis by RP-HPLC-DAD. KSU J Agric Nat. (2022) 25:10–8. 10.18016/ksutarimdoga.vi.875313 - DOI
-
- Oliff H. Scientific and clinical monograph for Pycnogenol. Austin, TX: American Botanical Council; (2019). p. 1–46.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

