Advanced Neuromorphic Applications Enabled by Synaptic Ion-Gating Vertical Transistors
- PMID: 38757653
- PMCID: PMC11251569
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202305611
Advanced Neuromorphic Applications Enabled by Synaptic Ion-Gating Vertical Transistors
Abstract
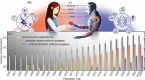
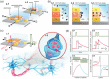
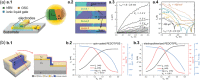
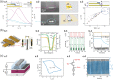
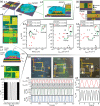
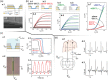
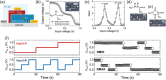
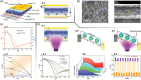
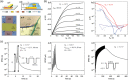
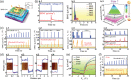
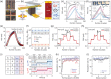
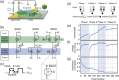
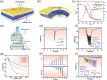
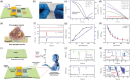
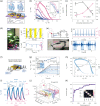
Bioinspired synaptic devices have shown great potential in artificial intelligence and neuromorphic electronics. Low energy consumption, multi-modal sensing and recording, and multifunctional integration are critical aspects limiting their applications. Recently, a new synaptic device architecture, the ion-gating vertical transistor (IGVT), has been successfully realized and timely applied to perform brain-like perception, such as artificial vision, touch, taste, and hearing. In this short time, IGVTs have already achieved faster data processing speeds and more promising memory capabilities than many conventional neuromorphic devices, even while operating at lower voltages and consuming less power. This work focuses on the cutting-edge progress of IGVT technology, from outstanding fabrication strategies to the design and realization of low-voltage multi-sensing IGVTs for artificial-synapse applications. The fundamental concepts of artificial synaptic IGVTs, such as signal processing, transduction, plasticity, and multi-stimulus perception are discussed comprehensively. The contribution draws special attention to the development and optimization of multi-modal flexible sensor technologies and presents a roadmap for future high-end theoretical and experimental advancements in neuromorphic research that are mostly achievable by the synaptic IGVTs.
Keywords: artificial synapses; brain‐inspired; electrochemical; field effects; human‐machine interfacing; multi‐modal; sensors.
© 2024 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Santiago R. Y. C., Textura del sistema nervioso del hombre y de los vertebrados, Librerıía de Nicolás Moya, España, Madrid, 1899.
-
- Kandel E. R. in Principles of Neural Science, 5th Ed., McGraw‐Hill, New York, 2013.
-
- Bhunia R., Boahen E. K., Kim D. J., Oh H., Kong Z., Kim D. H., J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 7485.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
