Isoflurane increases the activity of the vascular matrix metalloproteinase-2 in non-pregnant rats and increases the nitric oxide metabolites in pregnancy
- PMID: 38757914
- PMCID: PMC11147811
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20240192
Isoflurane increases the activity of the vascular matrix metalloproteinase-2 in non-pregnant rats and increases the nitric oxide metabolites in pregnancy
Abstract
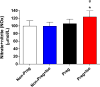
Surgeries that require general anesthesia occur in 1.5-2% of gestations. Isoflurane is frequently used because of its lower possibility of affecting fetal growth. Therefore, we examined the isoflurane anesthesia-induced effects on maternal hemodynamic and vascular changes. We hypothesized that isoflurane would enhance endothelium-dependent vasodilation as a consequence of increased nitric oxide and decreased metalloproteinases (MMPs). Female rats (n=28) were randomized into 4 groups (7 rats/group): conscious (non-anesthetized) non-pregnant group, non-pregnant anesthetized group, conscious pregnant group, and pregnant anesthetized group. Anesthesia was performed on the 20th pregnancy day, and hemodynamic parameters were monitored. Nitric oxide metabolites, gelatinolytic activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9, and the vascular function were assessed. Isoflurane caused no significant hemodynamic changes in pregnant compared with non-pregnant anesthetized group. Impaired acetylcholine-induced relaxations were observed only in conscious non-pregnant group (by approximately 62%) versus 81% for other groups. Phenylephrine-induced contractions were greater in endothelium-removed aorta segments of both pregnant groups (with or without isoflurane) compared with non-pregnant groups. Higher nitric oxide metabolites were observed in anesthetized pregnant in comparison with the other groups. Reductions in the 75 kDa activity and concomitant increases in 64 kDa MMP-2 isoforms were observed in aortas of pregnant anesthetized (or not) groups compared with conscious non-pregnant group. Isoflurane anesthesia shows stable effects on hemodynamic parameters and normal MMP-2 activation in pregnancy. Furthermore, there were increases in nitric oxide bioavailability, suggesting that isoflurane provides protective actions to the endothelium in pregnancy.
Keywords: isoflurane; metalloproteinase; nitric oxide; non-pregnant rats; pregnancy.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pregnancy hypertension-associated endothelial dysfunction is attenuated by isoflurane anesthesia: Evidence of protective effect related to increases in nitric oxide.Life Sci. 2023 Oct 15;331:122039. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.122039. Epub 2023 Aug 28. Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37648198
-
Sevoflurane and isoflurane anesthesia induce redox imbalance, but only sevoflurane impairs vascular contraction.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2023 Oct;37(5):937-946. doi: 10.1111/fcp.12901. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37085979
-
Effects of halothane and isoflurane on acetylcholine-induced, endothelium-dependent vasodilation in perfused rat mesenteric arterial beds.J Anesth. 2003;17(1):13-21. doi: 10.1007/s005400300003. J Anesth. 2003. PMID: 12908683
-
Reductions of Circulating Nitric Oxide are Followed by Hypertension during Pregnancy and Increased Activity of Matrix Metalloproteinases-2 and -9 in Rats.Cells. 2019 Nov 7;8(11):1402. doi: 10.3390/cells8111402. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31703340 Free PMC article.
-
Role of endothelium in the modulation of isoflurane-induced vasodilatation in rat thoracic aorta.Br J Anaesth. 1997 Jul;79(1):84-7. doi: 10.1093/bja/79.1.84. Br J Anaesth. 1997. PMID: 9301394
Cited by
-
The Complex Role of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) in Health and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 21;25(24):13691. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413691. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769454 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mata K.M., Li W., Reslan O.M., Siddiqui W.T., Opsasnick L.A. and Khalil R.A. (2015) Adaptive increases in expression and vasodilator activity of estrogen receptor subtypes in a blood vessel-specific pattern during pregnancy. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 309, 1679–1696 10.1152/ajpheart.00532.2015 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ren Z., Cui N., Zhu M. and Khalil R.A. (2018) Placental growth factor reverses decreased vascular and uteroplacental MMP-2 and MMP-9 and increased MMP-1 and MMP-7 and collagen types I and IV in hypertensive pregnancy. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 315, 33–47 10.1152/ajpheart.00045.2018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2019/06.072-0/Sao Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP)
- 2018/24.484-0 and 2021/08.380-3/Sao Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP)
- Finance Code 001/Coordenacao de Aperfeicoamento de Pessoal de Nivel Superior (CAPES)
- 305091/2021 and 406442/2022-3/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

