Prognostic value of serum oncomarkers for patients hospitalized with acute exacerbation of interstitial lung disease
- PMID: 38757948
- PMCID: PMC11102678
- DOI: 10.1177/17534666241250332
Prognostic value of serum oncomarkers for patients hospitalized with acute exacerbation of interstitial lung disease
Abstract
Background: Different types of inflammatory processes and fibrosis have been implicated in the pathogenesis of interstitial lung disease (ILD), a heterogeneous, diffuse, parenchymal lung disease. Acute exacerbation (AE) of ILD is characterized by significant respiratory deterioration and is associated with high mortality rates. Several serum oncomarkers have been used to determine the prognosis of ILD; however, the prognostic value of serum oncomarker levels in patients with AE-ILD remains unclear.
Objective: To evaluate the prognostic value of serum oncomarker levels in patients with AE-ILD and its main subtypes.
Design: Retrospective study.
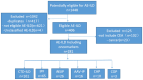
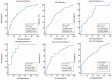
Methods: The serum levels of 8 oncomarkers in 281 patients hospitalized with AE-ILD at our institution between 2017 and 2022 were retrospectively reviewed. The baseline characteristics and serum oncomarker levels were compared between the survival and non-survival groups of AE-ILD and its main subtypes. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to identify independent prognosis-related markers, and the best prognostic predictor was analyzed using receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis.
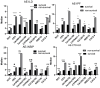
Result: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF; n = 65), idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (iNSIP; n = 26), and connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease (CTD-ILD; n = 161) were the three main subtypes of ILD. The in-hospital mortality rate among patients with AE-ILD was 21%. The serum oncomarker levels of most patients with AE-ILD and its main subtypes in the non-survival group were higher than those in the survival group. Multivariate analysis revealed that ferritin and cytokeratin 19 fragments (CYFRA21-1) were independent prognostic risk factors for patients hospitalized with AE-ILD or AE-CTD-ILD. CYFRA21-1 was identified as an independent prognostic risk factor for patients hospitalized with AE-IPF or AE-iNSIP.
Conclusion: CYFRA21-1 may be a viable biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with AE-ILD, regardless of the underlying subtype of ILD. Ferritin has a prognostic value in patients with AE-ILD or AE-CTD-ILD.
Keywords: acute exacerbation; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; interstitial lung disease; oncomarker; tumor marker.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Miyashita K, Kono M, Saito G, et al. Prognosis after acute exacerbation in patients with interstitial lung disease other than idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clin Respir J 2021; 15: 336–344. - PubMed
-
- Moua T, Westerly BD, Dulohery MM, et al. Patients with fibrotic interstitial lung disease hospitalized for acute respiratory worsening: a large cohort analysis. Chest 2016; 149: 1205–1214. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki A, Kondoh Y, Brown KK, et al. Acute exacerbations of fibrotic interstitial lung diseases. Respirology 2020; 25: 525–534. - PubMed
-
- Rusanov V, Kramer MR, Raviv Y, et al. The significance of elevated tumor markers among patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis before and after lung transplantation. Chest 2012; 141: 1047–1054. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

