Incidence of perioperative complications in COVID-19 survivors: Prospective observational clinical trial
- PMID: 38758840
- PMCID: PMC11098257
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038246
Incidence of perioperative complications in COVID-19 survivors: Prospective observational clinical trial
Abstract
Background: As long as the COVID-19 pandemic continued, the continuation of elective surgery had been unavoidable. There is still no consensus on the timing of elective surgery in patients who have recovered from COVID-19. The primary aim of this study was to determine the effect of time after COVID-19 infection on perioperative complications.
Methods: This prospective observational single center included adult patients who had recovered from COVID-19 and underwent surgery between February and July 2021. Data were prospectively collected from the patient and hospital database, the preoperative evaluation form and the perioperative anesthesia forms.
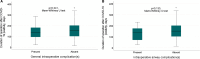
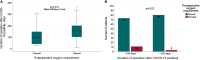
Results: A total of 167 patients were included in our study. Preoperative COVID-19 RT-PCR test results were negative in all patients. The mean time of positive COVID-19 diagnosis was 151.0 ± 74.0 days before the day of surgery. Intraoperative general and airway complications occurred in 33 (19.8%) and 17 (10.2%) patients, respectively. Although the time from COVID-19 positivity to surgery was shorter in patients with intraoperative general and airway complications, the difference between the groups did not reach statistical significance (P = .241 and P = .133, respectively). The median time from COVID-19 positivity to surgery in patients with and without postoperative complications was 156.0 (min: 27.0-max: 305.0) and 148.5 (min: 14.0-max: 164.0) days, respectively (P = .757). In patients with and without oxygen support in the postoperative period, the median time from COVID-19 positivity to surgery was 98.0 (min: 27.0-max: 305.0) and 154.0 (min: 14.0-max: 364.0) days, respectively. In patients who received oxygen support in the postoperative period, the time from COVID-19 positivity to surgery was shorter and the difference between the groups was statistically significant (P = .014).
Conclusions: The incidence of perioperative complications decreased with increasing time after a positive SARS-CoV-2 infection, but there was no difference in perioperative complications between the groups. As the time between COVID-19 positivity and surgery increased, the need for oxygen support in the postoperative period decreased. It is not possible to share clear data on the timing of operation after SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

