Deregulated miR-146a-3p alleviates disease progression in atherosclerosis through inactivating NF-κB: An experimental study
- PMID: 38758895
- PMCID: PMC11098229
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038061
Deregulated miR-146a-3p alleviates disease progression in atherosclerosis through inactivating NF-κB: An experimental study
Abstract
Background: Atherosclerosis (AS), as a complex chronic inflammatory disease, is 1 of the main causes of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. This study aimed to confirm the direct interaction between miR-146a-3p and NF-κB, and explore the role of miR-146a-3p/NF-κB in the regulation of inflammation in AS.
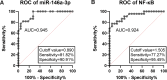
Methods: Bioinformatic prediction and dual-luciferase reporter assay were used to confirm the interaction between miR-146a-3p and NF-κB. Lipopolysaccharides stimulation was performed to establish AS inflammatory cell model, and the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines were estimated using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. miR-146a-3p and NF-κB expression were evaluated using reverse transcription quantitative PCR, and their clinical value was examined using a receiver operating characteristic curve.
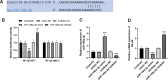
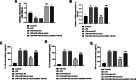
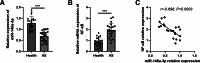
Results: Inflammatory cell model showed increased IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. NF-κB was a target gene of miR-146a-3p, and mediated the inhibitory effects of miR-146a-3p on inflammatory responses in the cell model. In patients with AS, miR-146a-3p/NF-κB was associated with patients' clinical data and inflammatory cytokine levels, and aberrant miR-146a-3p and NF-κB showed diagnostic accuracy to distinguish AS patients from healthy populations.
Conclusion: miR-146a-3p might inhibit inflammation by targeting NF-κB in AS progression, and miR-146a-3p/ NF-κB might provide novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets for the prevention of AS and related vascular events.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Wu S, Wu B, Liu M, et al. . Stroke in China: advances and challenges in epidemiology, prevention, and management. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:394–405. - PubMed
-
- Saini V, Guada L, Yavagal DR. Global epidemiology of stroke and access to acute ischemic stroke interventions. Neurology. 2021;97(20 Suppl 2):S6–S16. - PubMed
-
- Heck D, Jost A. Carotid stenosis, stroke, and carotid artery revascularization. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2021;65:49–54. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

