Deciphering the progression of fine-needle aspiration: A bibliometric analysis of thyroid nodule research
- PMID: 38758913
- PMCID: PMC11098219
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038059
Deciphering the progression of fine-needle aspiration: A bibliometric analysis of thyroid nodule research
Abstract
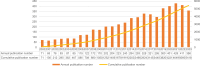
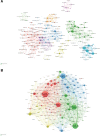
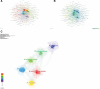
This study aims to dissect the evolution and pivotal shifts in Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) research for thyroid nodules over the past 2 decades, focusing on delineating key technological advancements and their impact on clinical practice. A comprehensive bibliometric analysis was conducted on 5418 publications from the Web of Science Core Collection database (2000-2023). Publications were rigorously selected based on their contributions to the advancement of FNA techniques and their influence on thyroid nodule management practices. Our analysis uncovered significant breakthroughs, most notably the incorporation of ultrasound and molecular diagnostics in FNA, which have markedly elevated diagnostic accuracy. A pivotal shift was identified towards minimally invasive post-FNA treatments, such as Radiofrequency Ablation, attributable to these diagnostic advancements. Additionally, the emergence of AI-assisted cytology represents a frontier in precision diagnostics, promising enhanced disease identification. The geographical analysis pinpointed the United States, Italy, and China as key contributors, with the United States leading in both publication volume and citation impact. This bibliometric analysis sheds light on the transformative progression in FNA practices for thyroid nodules, characterized by innovative diagnostic technologies and a trend towards patient-centric treatment approaches. The findings underscore the need for further research into AI integration and global practice standardization. Future explorations should focus on the practical application of these advancements in diverse healthcare settings and their implications for global thyroid nodule management.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A Bibliometric Analysis of 8271 Publications on Thyroid Nodules From 2000 to 2021.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Apr 21;13:845776. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.845776. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35528005 Free PMC article.
-
US of thyroid nodules: can AI-assisted diagnostic system compete with fine needle aspiration?Eur Radiol. 2024 Feb;34(2):1324-1333. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-10132-1. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37615763
-
Repeat Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology Refines the Selection of Thyroid Nodules for Afirma Gene Expression Classifier Testing.Thyroid. 2021 Aug;31(8):1253-1263. doi: 10.1089/thy.2020.0969. Epub 2021 Jun 22. Thyroid. 2021. PMID: 33813868 Free PMC article.
-
Current status of fine needle aspiration for thyroid nodules.Adv Surg. 2006;40:223-38. doi: 10.1016/j.yasu.2006.06.003. Adv Surg. 2006. PMID: 17163105 Review.
-
Molecular profiling of thyroid nodule fine-needle aspiration cytology.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017 Jul;13(7):415-424. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.24. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28361927 Review.
Cited by
-
Application progress of artificial intelligence in managing thyroid disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 17;16:1578455. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1578455. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40600013 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rossi ED, Tralongo P, Fiorentino V, et al. . Approach to FNA of thyroid gland cysts. Adv Anat Pathol. 2022;29:358–64. - PubMed
-
- Wong R, Farrell SG, Grossmann M. Thyroid nodules: diagnosis and management. Med J Aust. 2018;209:92–8. - PubMed
-
- Chen DW, Lang BHH, McLeod DSA, Newbold K, Haymart MR. Thyroid cancer. Lancet. 2023;401:1531–44. - PubMed
-
- Alexander EK, Cibas ES. Diagnosis of thyroid nodules. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022;10:533–9. - PubMed
-
- Kobaly K, Kim CS, Mandel SJ. Contemporary management of thyroid nodules. Annu Rev Med. 2022;73:517–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

