Prediction analysis of carbon emission in China's electricity industry based on the dual carbon background
- PMID: 38758945
- PMCID: PMC11101092
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302068
Prediction analysis of carbon emission in China's electricity industry based on the dual carbon background
Abstract
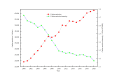
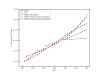
The electric power sector is the primary contributor to carbon emissions in China. Considering the context of dual carbon goals, this paper examines carbon emissions within China's electricity sector. The research utilizes the LMDI approach for methodological rigor. The results show that the cumulative contribution of economies scale, power consumption factors and energy structure are 114.91%, 85.17% and 0.94%, which contribute to the increase of carbon emissions, the cumulative contribution of power generation efficiency and ratio of power dissipation to generation factor are -19.15% and -0.01%, which promotes the carbon reduction. The decomposition analysis highlights the significant influence of economic scale on carbon emissions in the electricity industry, among the seven factors investigated. Meanwhile, STIRPAT model, Logistic model and GM(1,1) model are used to predict carbon emissions, the average relative error between actual carbon emissions and the predicted values are 0.23%, 8.72% and 7.05%, which indicates that STIRPAT model is more suitable for medium- to long-term predictions. Based on these findings, the paper proposes practical suggestions to reduce carbon emissions and achieve the dual carbon goals of the power industry.
Copyright: © 2024 Ding et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Xiao-ling Ge, Yang Wang, Hong-qing Zhu, Zequn Ding. Analysis and forecast of the Tianjin industrial carbon dioxide emissions resulted from energy consumption. International Journal of Sustainable Energy 36 (7), 637–653.
-
- National Bureau of Statistics (NBS). International Statistical Yearbook 2013.China Statistics: Press 2013; Beijing.
-
- Sheng Zhou, Qing Tong, Sha Yu, Yu Wang, Qi-min Chai, Xi-liang Zhang. Role of non-fossil energy in meeting China’s energy and climate target for 2020. Energy Policy 51, 14–17.
-
- Lin Zeng, Ming Xu, Sai Liang, Si-yu Zeng, Tian-zhu Zhang. Revisiting drivers of energy intensity in China during 1997–2007: A structural decomposition analysis. Energy Policy 67, 640–647.
-
- Hongqing Zhu, Xiaoling Ge, Yang Wang, Zequn Ding. Analysis and forecast of Tianjin’s industrial energy consumption. International Journal of Energy Sector Management,11(1),46–64.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

