Exploring active ingredients and mechanisms of Coptidis Rhizoma-ginger against colon cancer using network pharmacology and molecular docking
- PMID: 38759074
- PMCID: PMC11191530
- DOI: 10.3233/THC-248046
Exploring active ingredients and mechanisms of Coptidis Rhizoma-ginger against colon cancer using network pharmacology and molecular docking
Abstract
Background: Colon cancer is the most prevalent and rapidly increasing malignancy globally. It has been suggested that some of the ingredients in the herb pair of Coptidis Rhizoma and ginger (Zingiber officinale), a traditional Chinese medicine, have potential anti-colon cancer properties.
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying the effects of the Coptidis Rhizoma-ginger herb pair in treating colon cancer, using an integrated approach combining network pharmacology and molecular docking.
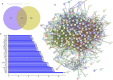
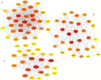
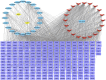
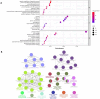
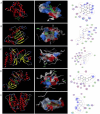
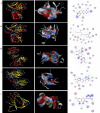
Methods: The ingredients of the herb pair Coptidis Rhizoma-ginger, along with their corresponding protein targets, were obtained from the Traditional Chinese Medicine System Pharmacology and Swiss Target Prediction databases. Target genes associated with colon cancer were retrieved from the GeneCards and OMIM databases. Then, the protein targets of the active ingredients in the herb pair were identified, and the disease-related overlapping targets were determined using the Venn online tool. The protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed using STRING database and analyzed using Cytoscape 3.9.1 to identify key targets. Then, a compound-target-disease-pathway network map was constructed. The intersecting target genes were subjected to Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses for colon cancer treatment. Molecular docking was performed using the Molecular Operating Environment (MOE) software to predict the binding affinity between the key targets and active compounds.
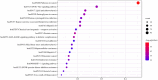
Results: Besides 1922 disease-related targets, 630 targets associated with 20 potential active compounds of the herb pair Coptidis Rhizoma-ginger were collected. Of these, 229 intersection targets were obtained. Forty key targets, including STAT3, Akt1, SRC, and HSP90AA1, were further analyzed using the ClueGO plugin in Cytoscape. These targets are involved in biological processes such as miRNA-mediated gene silencing, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling, and telomerase activity. KEGG enrichment analysis showed that PI3K-Akt and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) signaling pathways were closely related to colon cancer prevention by the herb pair Coptidis Rhizoma-ginger. Ten genes (Akt1, TP53, STAT3, SRC, HSP90AA1, JAK2, CASP3, PTGS2, BCl2, and ESR1) were identified as key genes for validation through molecular docking simulation.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that the herb pair Coptidis Rhizoma-ginger exerted preventive effects against colon cancer by targeting multiple genes, utilizing various active compounds, and modulating multiple pathways. These findings might provide the basis for further investigations into the molecular mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects of Coptidis Rhizoma-ginger in colon cancer treatment, potentially leading to the development of novel drugs for combating this disease.
Keywords: Colon cancer; Coptidis Rhizoma; ginger; molecular docking; network pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
None to report.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Mechanism of Action of the Active Ingredients of Coptidis rhizoma against Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Was Investigated Using Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Technology.Viruses. 2024 Jul 31;16(8):1229. doi: 10.3390/v16081229. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39205203 Free PMC article.
-
[Prediction of mechanism of ginger-processed Anemarrhenae Rhizoma in intervening in cough due to cold and dampness in lung based on network pharmacology].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 Oct;49(20):5460-5468. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240716.304. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39701729 Chinese.
-
Investigating the Mechanism of Rhizoma Coptidis-Eupatorium fortunei Medicine in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Nov 21;2022:7978258. doi: 10.1155/2022/7978258. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36452059 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the mechanism of action of Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder in colorectal cancer based on network pharmacology and molecular docking studies.Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2023 Oct;39(2):1107-1127. doi: 10.1080/02648725.2023.2167765. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2023. PMID: 36735641 Review.
-
Elucidation of the mechanism of Zhenbao pills for the treatment of spinal cord injury by network pharmacology and molecular docking: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Feb 16;103(7):e36970. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036970. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38363936 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boman B, Huang E. Human colon cancer stem cells: a new paradigm in gastrointestinal oncology. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26: 2828-38. - PubMed
-
- Chen YX, Gao QY, Zou TH, et al. Berberine versus placebo for the prevention of recurrence of colorectal adenoma: a multicentre, double-blinded, randomised controlled study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. Mar; 5(3): 267-275. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30409-1. Epub 2020 Jan 8. PMID: 31926918. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

