The E592K variant of SF3B1 creates unique RNA missplicing and associates with high-risk MDS without ring sideroblasts
- PMID: 38759096
- PMCID: PMC11331715
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023011260
The E592K variant of SF3B1 creates unique RNA missplicing and associates with high-risk MDS without ring sideroblasts
Abstract
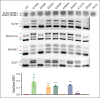
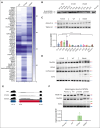
Among the most common genetic alterations in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are mutations in the spliceosome gene SF3B1. Such mutations induce specific RNA missplicing events, directly promote ring sideroblast (RS) formation, and generally associate with a more favorable prognosis. However, not all SF3B1 mutations are the same, and little is known about how distinct hotspots influence disease. Here, we report that the E592K variant of SF3B1 associates with high-risk disease features in MDS, including a lack of RS, increased myeloblasts, a distinct comutation pattern, and a lack of favorable survival seen with other SF3B1 mutations. Moreover, compared with other hot spot SF3B1 mutations, E592K induces a unique RNA missplicing pattern, retains an interaction with the splicing factor SUGP1, and preserves normal RNA splicing of the sideroblastic anemia genes TMEM14C and ABCB7. These data have implications for our understanding of the functional diversity of spliceosome mutations, as well as the pathobiology, classification, prognosis, and management of SF3B1-mutant MDS.
© 2024 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: T.J. received institutional research support from CTI Biopharma, Kartos Therapeutics, Incyte, and Bristol Myers Squibb, and has been a participant on the advisory boards with Bristol Myers Squibb, Incyte, AbbVie, CTI Biopharma, Kite, Cogent Biosciences, Blueprint Medicine, Telios Pharma, Protagonist Therapeutics, Galapagos, TScan Therapeutics, Karyopharm, and MorphoSys. S.F. has consulted for and received honoraria from Blueprint Medicine, CTI Biopharma, Sobi, Bristol Myers Squibb, AbbVie, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Incyte, Janssen, Jazz, Karyopharm, Novartis, PharmaEssentia, Sanofi, Servier, Stemline, Taiho, and Takeda. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures





Update of
-
The E592K variant of SF3B1 creates unique RNA missplicing and associates with high-risk MDS without ring sideroblasts.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 14:rs.3.rs-2802265. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2802265/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Blood Adv. 2024 Aug 13;8(15):3961-3971. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023011260. PMID: 37090662 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Darman RB, Seiler M, Agrawal AA, et al. Cancer-associated SF3B1 hotspot mutations induce cryptic 3′ splice site selection through use of a different branch point. Cell Rep. 2015;13(5):1033–1045. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

