DARE-ISC model for prediction of 1-year ischaemic stroke risk in the general population and atrial fibrillation patients: a Danish nationwide cohort study
- PMID: 38760046
- PMCID: PMC11103190
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-076640
DARE-ISC model for prediction of 1-year ischaemic stroke risk in the general population and atrial fibrillation patients: a Danish nationwide cohort study
Abstract
Objectives: To develop a risk assessment model (DAnish REgister Ischaemic Stroke Classifier, DARE-ISC) for predicting 1-year primary ischaemic stroke/systemic embolism (SE) in the general population. Secondly, to validate the accuracy DARE-ISC in atrial fibrillation (AF) patients where well-established models and risk scores exist.
Design: Retrospective cohort study. DARE-ISC was developed using gradient boosting decision trees with information from 375 covariates including baseline information on relevant diagnoses, demographic characteristics, registered health-services, lifestyle-related covariates, hereditary stroke components, drug prescriptions and stress proxies.
Setting: Danish nationwide registries.
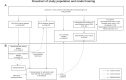
Participants: All Danish individuals aged ≥18 from 2010 to 2017 (n=35 519 348 person-years). The model was trained on the 2010-2016 cohorts with validation in the 2017 cohort.
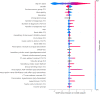
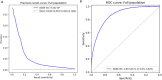
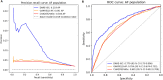
Primary and secondary outcome measures: Model optimisation and validation were performed through comparison of the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) and average precision scores. Additionally, the relative importance of the model covariates was derived using SHAP values.
Results: DARE-ISC had an AUC (95% CI) of 0.874 (0.871 to 0.876) in the general population. In AF patients, DARE-ISC was superior to the GARFIELD-AF risk model and CHA2DS2-VASc score with AUC of 0.779 (95% CI 0.75 to 0.806), 0.704 (95% CI 0.674 to 0.732) and 0.681 (95% CI 0.652 to 0.709), respectively. Furthermore, in AF patients, DARE-ISC had an average threefold and fourfold higher ratio of correctly identified strokes compared with the GARFIELD-AF risk model and CHA2DS2-VASc score, as indicated by average precision scores of 0.119, 0.041 and 0.034, respectively.
Conclusions: DARE-ISC had a very high stroke prediction accuracy in the general population and was superior to the GARFIELD-AF risk model and CHA2DS2-VASc score for predicting ischaemic stroke/SE in AF patients.
Keywords: cardiac epidemiology; epidemiology; stroke.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: SW reports separate funding from the Novo Nordisk Foundation within the last 36 months. Other authors have nothing to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GARFIELD-AF model for prediction of stroke and major bleeding in atrial fibrillation: a Danish nationwide validation study.BMJ Open. 2019 Nov 11;9(11):e033283. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-033283. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31719095 Free PMC article.
-
Improved risk stratification of patients with atrial fibrillation: an integrated GARFIELD-AF tool for the prediction of mortality, stroke and bleed in patients with and without anticoagulation.BMJ Open. 2017 Dec 21;7(12):e017157. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-017157. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 29273652 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the CHA2DS2-VASc Score in Predicting Ischemic Stroke, Thromboembolism, and Death in Patients With Heart Failure With and Without Atrial Fibrillation.JAMA. 2015 Sep 8;314(10):1030-8. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.10725. JAMA. 2015. PMID: 26318604
-
A new score with superior stroke risk prediction in atrial fibrillation: entropy-based information gain approaches in a large nationwide cohort.J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2025 May 14. doi: 10.1007/s10840-025-02053-4. Online ahead of print. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2025. PMID: 40369260 Review.
-
Stroke Risk in Atrial Fibrillation: Beyond the CHA2DS2-VASc Score.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2019 Jul 27;21(9):95. doi: 10.1007/s11886-019-1189-6. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31352536 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of atrial fibrillation in vascular cognitive impairment and dementia: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and preventive strategies.Geroscience. 2025 Feb;47(1):287-300. doi: 10.1007/s11357-024-01290-1. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Geroscience. 2025. PMID: 39138793 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fox KAA, Lucas JE, Pieper KS, et al. . Improved risk stratification of patients with atrial fibrillation: an integrated GARFIELD-AF tool for the prediction of mortality, stroke and bleed in patients with and without anticoagulation. BMJ Open 2017;7:e017157. 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-017157 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
