Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting the occurrence of renal dysfunction after treatment of immune checkpoint inhibitor: a retrospective case-control study
- PMID: 38760047
- PMCID: PMC11103235
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-082484
Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting the occurrence of renal dysfunction after treatment of immune checkpoint inhibitor: a retrospective case-control study
Abstract
Purpose: The administration of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) may lead to renal adverse events, notably including renal dysfunction. To early predict the probability of renal dysfunction after ICIs therapy, a retrospective case-control study was conducted.
Methods: Clinical information on ICIs-treated patients was collected. Multivariable logistic regression was applied to identify risk factors for renal dysfunction after ICIs treatment. Moreover, a nomogram model was developed and validated internally.
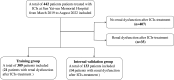
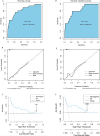
Results: A total of 442 patients were included, among which 35 (7.9%) experienced renal dysfunction after ICIs treatment. Lower baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) (OR 0.941; 95% CI 0.917 to 0.966; p<0.001), concurrent exposure of platinum(OR 4.014; 95% CI 1.557 to 10.346; p=0.004), comorbidities of hypertension (OR 3.478; 95% CI 1.600 to 7.562; p=0.002) and infection (OR 5.402; 95% CI 1.544 to 18.904; p=0.008) were found to be independent associated with renal dysfunction after ICIs treatment. To develop a predictive nomogram for the occurrence of renal dysfunction after ICIs treatment, the included cases were divided into training and validation groups in a ratio of 7:3 randomly. The above four independent risk factors were included in the model. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curves of the predictiive model were 0.822 (0.723-0.922) and 0.815 (0.699-0.930) in the training and validation groups, respectively.
Conclusions: Lower baseline eGFR, platinum exposure, comorbidities of hypertension and infection were predictors of renal dysfunction in ICIs-treated patients with cancer. A nomogram was developed to predict the probability of renal dysfunction after ICIs treatment, which might be operable and valuable in clinical practice.
Keywords: IMMUNOLOGY; Nephrology; ONCOLOGY; Pharmacology; Risk Factors.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
