Imaging Assessment of Radiation Therapy-Related Normal Tissue Injury in Children: A PENTEC Visionary Statement
- PMID: 38760116
- PMCID: PMC11684541
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2024.03.006
Imaging Assessment of Radiation Therapy-Related Normal Tissue Injury in Children: A PENTEC Visionary Statement
Abstract
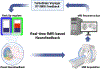
The Pediatric Normal Tissue Effects in the Clinic (PENTEC) consortium has made significant contributions to understanding and mitigating the adverse effects of childhood cancer therapy. This review addresses the role of diagnostic imaging in detecting, screening, and comprehending radiation therapy-related late effects in children, drawing insights from individual organ-specific PENTEC reports. We further explore how the development of imaging biomarkers for key organ systems, alongside technical advancements and translational imaging approaches, may enhance the systematic application of imaging evaluations in childhood cancer survivors. Moreover, the review critically examines knowledge gaps and identifies technical and practical limitations of existing imaging modalities in the pediatric population. Addressing these challenges may expand access to, minimize the risk of, and optimize the real-world application of, new imaging techniques. The PENTEC team envisions this document as a roadmap for the future development of imaging strategies in childhood cancer survivors, with the overarching goal of improving long-term health outcomes and quality of life for this vulnerable population.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
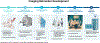

References
-
- Constine LS, et al., Pediatric Normal Tissue Effects in the Clinic (PENTEC): An International Collaboration to Assess Normal Tissue Radiation Dose-Volume-Response Relationships for Children With Cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2021. - PubMed
-
- Olch AJ, et al., Physics Considerations for Evaluation of Dose for Dose-Response Models of Pediatric Late Effects From Radiation Therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2023. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

