The Effect of Bovine Trypsin on the Adhesion and pH of Dental Plaque Biofilms: An In Vitro Study
- PMID: 38760192
- PMCID: PMC11551584
- DOI: 10.1016/j.identj.2024.04.025
The Effect of Bovine Trypsin on the Adhesion and pH of Dental Plaque Biofilms: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of bovine trypsin on the adhesion and pH of dental plaque biofilms.
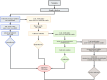
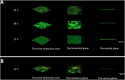
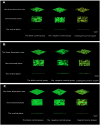
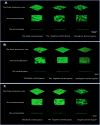
Methods: A multispecies dental plaque biofilm model and a single-species dental plaque biofilm model were established in vitro. Three groups were tested: (1) blank control group (aseptic ultrapure water); (2) negative control group (1M Tris-HCl buffer, pH = 7.4); and (3) experimental group (bovine trypsin). Adhesion ability was measured using an automatic microplate reader and visualised by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). The pH was measured using a pH meter. The expression of gtfB, gtfC, and gtfD was analysed using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.
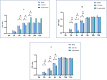
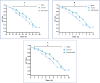
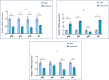
Results: Adhesion ability in the experimental group was significantly lower than that in the blank group and the negative control group (P < .05); readhesion ability in the experimental group was inhibited for a certain period of time (24-hour multispecies biofilms were inhibited from 4 to 8 hours, and the 48- and 72-hour multispecies biofilms were inhibited from 2 to 6 hours; P < .05). The decrease in pH was inhibited for a certain period of time (24-hour multispecies biofilms were inhibited from 2 to 8 hours, and the 48- and 72-hour multispecies biofilms were inhibited from 1 to 8 hours; P < .05). Expression levels of gtfB, gtfC, gtfD, and ldh in the experimental group were significantly lower than those in the blank group (P < .05).
Conclusions: Bacterial adhesion, and readhesion, decreasd pH, and expression of adhesion- and acid-related genes by Streptococcus mutans in biofilms could be reduced by bovine trypsin for a certain period of time.
Keywords: Adhesion; Bovine trypsin; Dental caries; Dental plaque biofilms; pH.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest None disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of arginine on the growth and biofilm formation of oral bacteria.Arch Oral Biol. 2017 Oct;82:256-262. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2017.06.026. Epub 2017 Jun 24. Arch Oral Biol. 2017. PMID: 28668766
-
The effect of bovine trypsin on dental biofilm dispersion: an in vitro study.Odontology. 2024 Apr;112(2):501-511. doi: 10.1007/s10266-023-00869-y. Epub 2023 Nov 13. Odontology. 2024. PMID: 37955766
-
Effect of antibacterial dental adhesive on multispecies biofilms formation.J Dent Res. 2015 Apr;94(4):622-9. doi: 10.1177/0022034515571416. Epub 2015 Feb 24. J Dent Res. 2015. PMID: 25715378 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Antimicrobial Peptide GH12 on the Cariogenic Properties and Composition of a Cariogenic Multispecies Biofilm.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Nov 30;84(24):e01423-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01423-18. Print 2018 Dec 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30341079 Free PMC article.
-
Biology of Streptococcus mutans-derived glucosyltransferases: role in extracellular matrix formation of cariogenic biofilms.Caries Res. 2011;45(1):69-86. doi: 10.1159/000324598. Epub 2011 Feb 23. Caries Res. 2011. PMID: 21346355 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

