Cardiovascular Risk Estimation Is Suboptimal in People With HIV
- PMID: 38761071
- PMCID: PMC11179796
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.123.029228
Cardiovascular Risk Estimation Is Suboptimal in People With HIV
Abstract
Background: Established cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk prediction functions may not accurately predict CVD risk in people with HIV. We assessed the performance of 3 CVD risk prediction functions in 2 HIV cohorts.
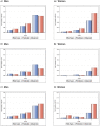
Methods and results: CVD risk scores were calculated in the Mass General Brigham and Kaiser Permanente Northern California HIV cohorts, using the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association atherosclerotic CVD function, the FHS (Framingham Heart Study) hard coronary heart disease function and the Framingham Heart Study hard CVD function. Outcomes were myocardial infarction or coronary death for FHS hard coronary heart disease function; and myocardial infarction, stroke, or coronary death for American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association and FHS hard CVD function. We calculated regression coefficients and assessed discrimination and calibration by sex; predicted to observed risk of outcome was also compared. In the combined cohort of 9412, 158 (1.7%) had a coronary heart disease event, and 309 (3.3%) had a CVD event. Among women, CVD risk was generally underestimated by all 3 risk functions. Among men, CVD risk was underestimated by the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association and FHS hard CVD function, but overestimated by the FHS hard coronary heart disease function. Calibration was poor for women using the FHS hard CVD function and for men using all functions. Discrimination in all functions was good for women (c-statistics ranging from 0.78 to 0.90) and moderate for men (c-statistics ranging from 0.71 to 0.72).
Conclusions: Established CVD risk prediction functions generally underestimate risk in people with HIV. Differences in model performance by sex underscore the need for both HIV-specific and sex-specific functions. Development of CVD risk prediction models tailored to HIV will enhance care for aging people with HIV.
Keywords: HIV; aging; cardiovascular; risk prediction.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

