The role of the early video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery in children with pleural empyema
- PMID: 38761186
- PMCID: PMC11102380
- DOI: 10.1007/s00383-024-05715-y
The role of the early video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery in children with pleural empyema
Abstract
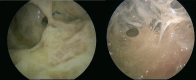
Purpose: Pleural empyema (PE) is a collection of purulent material in the pleural space. PE's management in children is a challenge and an inappropriate diagnostic-therapeutic work up can lead to serious short and long-term complications. The aim of this study is to define the correct timing to approach a pediatric PE by video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS).
Methods: A retrospective observational study was conducted including pediatric patients who underwent video-assisted thoracoscopy for pleural empyema between May 2005 and September 2022.
Results: 62 patients were subjected to VATS for PE (32 in Group Early VATS, 30 in Group Late VATS). It emerged that the elapsed period between the onset of symptoms and surgery correlates in a statistically significant way with the post-operative stay in intensive care (z score 4.3 and p value < 0.0001) and the analysis between early VATS, late VATS and postoperative hospitalization showed a statistically significant reduction of the post-operative hospitalization in the early VATS groups (p value < 0.02).
Conclusions: VATS resulted to be safe and effective for the treatment of PE in children, and an early minimally invasive thoracoscopic intervention (early VATS) correlates with better outcomes, specifically in terms of intensive care hospitalization and overall hospitalization.
Keywords: Children; Minimally invasive surgery; Pleural empyema; Thoracoscopy; VATS; Video assisted thoracoscopic surgery.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Balachandran A, Shivbalan S, Thangavelu S, Vijayasekaran D, Subramnayam L (2003) Empyema thoracis. Indian J Pediatr 70(10):803–806. 10.1007/BF02723802 - PubMed
-
- Anastasi G, Cannas M, Cavaletti G, Cinti S, Manzoli L, Miscia S, Sbarbati A, Zecchi SA (2021) Trattato di Anatomia Umana 2021 + Atlante di Anatomia Umana ( Anatomy Bag Plus ) Edi-Ermes. Edi-Ermes.
-
- Spencer DA, Cliff D (2008) The changing epidemiology of parapneumonic empyema in children. Paediatr Child Health 18(11):513–518. 10.1016/j.paed.2008.07.013
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources