Two novel in vitro assays to screen chemicals for their capacity to inhibit thyroid hormone transmembrane transporter proteins OATP1C1 and OAT4
- PMID: 38761188
- PMCID: PMC11324666
- DOI: 10.1007/s00204-024-03787-2
Two novel in vitro assays to screen chemicals for their capacity to inhibit thyroid hormone transmembrane transporter proteins OATP1C1 and OAT4
Abstract
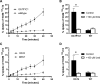
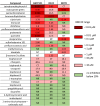
Early brain development depends on adequate transport of thyroid hormones (THs) from the maternal circulation to the fetus. To reach the fetal brain, THs have to cross several physiological barriers, including the placenta, blood-brain-barrier and blood-cerebrospinal fluid-barrier. Transport across these barriers is facilitated by thyroid hormone transmembrane transporters (THTMTs). Some endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) can interfere with the transport of THs by THTMTs. To screen chemicals for their capacity to disrupt THTMT facilitated TH transport, in vitro screening assays are required. In this study, we developed assays for two THTMTs, organic anion transporter polypeptide 1C1 (OATP1C1) and organic anion transporter 4 (OAT4), both known to play a role in the transport of THs across barriers. We used overexpressing cell models for both OATP1C1 and OAT4, which showed an increased uptake of radiolabeled T4 compared to control cell lines. Using these models, we screened various reference and environmental chemicals for their ability to inhibit T4 uptake by OATP1C1 and OAT4. Tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) was identified as an OATP1C1 inhibitor, more potent than any of the reference chemicals tested. Additionally perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS), perfluoroctanic acid (PFOA), pentachlorophenol and quercetin were identified as OATP1C1 inhibitors in a similar range of potency to the reference chemicals tested. Bromosulfophthalein, TBBPA, PFOA and PFOS were identified as potent OAT4 inhibitors. These results demonstrate that EDCs commonly found in our environment can disrupt TH transport by THTMTs, and contribute to the identification of molecular mechanisms underlying TH system disruption chemicals.
Keywords: Endocrine disrupting chemicals; In vitro bioassays; Organic anion transporter 4; Organic anion transporter polypeptide 1C1; Thyroid hormones.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of thyroid hormone transport in a human choroid plexus papilloma cell line (HIBCPP) as an in vitro blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier model.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2025 Feb 1;597:112449. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2024.112449. Epub 2024 Dec 29. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2025. PMID: 39740754
-
Organic anion transporter 4 (OAT 4) modifies placental transfer of perfluorinated alkyl acids PFOS and PFOA in human placental ex vivo perfusion system.Placenta. 2015 Oct;36(10):1185-91. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2015.07.119. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Placenta. 2015. PMID: 26303760
-
Thyroid hormone transport and metabolism by organic anion transporter 1C1 and consequences of genetic variation.Endocrinology. 2008 Oct;149(10):5307-14. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-0430. Epub 2008 Jun 19. Endocrinology. 2008. PMID: 18566113
-
Cellular entry of thyroid hormones by organic anion transporting polypeptides.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007 Jun;21(2):209-21. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2007.03.004. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007. PMID: 17574004 Review.
-
Zebrafish - An emerging model to explore thyroid hormone transporters and psychomotor retardation.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017 Dec 25;459:53-58. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2017.03.004. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28274736 Review.
Cited by
-
LC-HRMS analysis of ultrashort- and short-chain PFAS on porous graphitic carbon column and study of accumulation in plants.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2025 Aug 28. doi: 10.1007/s00216-025-06080-y. Online ahead of print. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2025. PMID: 40875007
-
A 2024 inventory of test methods relevant to thyroid hormone system disruption for human health and environmental regulatory hazard assessment.Open Res Eur. 2024 Nov 6;4:242. doi: 10.12688/openreseurope.18739.1. eCollection 2024. Open Res Eur. 2024. PMID: 39931575 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bakos É, Német O, Patik I, Kucsma N, Várady G, Szakács G, Özvegy-Laczka C (2020) A novel fluorescence-based functional assay for human OATP1A2 and OATP1C1 identifies interaction between third-generation P-gp inhibitors and OATP1A2. FEBS J 287(12):2468–2485. 10.1111/febs.15156 10.1111/febs.15156 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Buckalew AR, Wang J, Murr AS, Deisenroth C, Stewart WM, Stoker TE, Laws SC (2020) Evaluation of potential sodium-iodide symporter (NIS) inhibitors using a secondary Fischer rat thyroid follicular cell (FRTL-5) radioactive iodide uptake (RAIU) assay. Arch Toxicol 94(3):873–885. 10.1007/s00204-020-02664-y 10.1007/s00204-020-02664-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

