Polyamines: the pivotal amines in influencing the tumor microenvironment
- PMID: 38761252
- PMCID: PMC11102423
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-024-01034-9
Polyamines: the pivotal amines in influencing the tumor microenvironment
Abstract
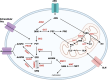
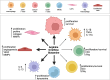
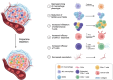
Cellular proliferation, function and survival is reliant upon maintaining appropriate intracellular polyamine levels. Due to increased metabolic needs, cancer cells elevate their polyamine pools through coordinated metabolism and uptake. High levels of polyamines have been linked to more immunosuppressive tumor microenvironments (TME) as polyamines support the growth and function of many immunosuppressive cell types such as MDSCs, macrophages and regulatory T-cells. As cancer cells and other pro-tumorigenic cell types are highly dependent on polyamines for survival, pharmacological modulation of polyamine metabolism is a promising cancer therapeutic strategy. This review covers the roles of polyamines in various cell types of the TME including both immune and stromal cells, as well as how competition for nutrients, namely polyamine precursors, influences the cellular landscape of the TME. It also details the use of polyamines as biomarkers and the ways in which polyamine depletion can increase the immunogenicity of the TME and reprogram tumors to become more responsive to immunotherapy.
Keywords: Amino acid metabolism; Immunotherapy; Polyamine; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The Casero and Stewart laboratory receives research funding through a sponsored research agreement with Panbela Therapeutics, Inc. and USWorldMeds. The funding sources were not involved in the development or writing of this review.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
