HyperMRI: hyperspectral and magnetic resonance fusion methodology for neurosurgery applications
- PMID: 38761318
- PMCID: PMC11230967
- DOI: 10.1007/s11548-024-03102-5
HyperMRI: hyperspectral and magnetic resonance fusion methodology for neurosurgery applications
Abstract
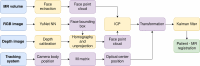
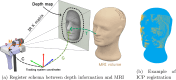
Purpose: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a common technique in image-guided neurosurgery (IGN). Recent research explores the integration of methods like ultrasound and tomography, among others, with hyperspectral (HS) imaging gaining attention due to its non-invasive real-time tissue classification capabilities. The main challenge is the registration process, often requiring manual intervention. This work introduces an automatic, markerless method for aligning HS images with MRI.
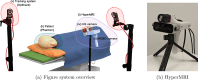
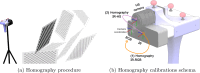
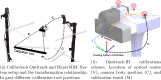
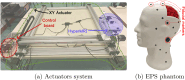
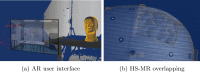
Methods: This work presents a multimodal system that combines RGB-Depth (RGBD) and HS cameras. The RGBD camera captures the patient's facial geometry, which is used for registration with the preoperative MR through ICP. Once MR-depth registration is complete, the integration of HS data is achieved using a calibrated homography transformation. The incorporation of external tracking with a novel calibration method allows camera mobility from the registration position to the craniotomy area. This methodology streamlines the fusion of RGBD, HS and MR images within the craniotomy area.
Results: Using the described system and an anthropomorphic phantom head, the system has been characterised by registering the patient's face in 25 positions and 5 positions resulted in a fiducial registration error of 1.88 ± 0.19 mm and a target registration error of 4.07 ± 1.28 mm, respectively.
Conclusions: This work proposes a new methodology to automatically register MR and HS information with a sufficient accuracy. It can support the neurosurgeons to guide the diagnosis using multimodal data over an augmented reality representation. However, in its preliminary prototype stage, this system exhibits significant promise, driven by its cost-effectiveness and user-friendly design.
Keywords: Computer-assisted intervention; Hyperspectral; Image registration; MRI.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- BRAINLAB AG (2006) Tracking system for medical equipment with infrared transmission. Published as EP1733693A1
-
- Choi S, Zhou QY, Koltun V (2015) Robust reconstruction of indoor scenes. 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7299195
-
- Claus D, Fitzgibbon AW (2005) A rational function lens distortion model for general cameras. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 213–219
-
- Drouin S, Kersten-Oertel M, Chen SJS, Collins DL (2012) A realistic test and development environment for mixed reality in neurosurgery. 10.1007/978-3-642-32630-1_2
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

