Liquid-liquid phase separation in innate immunity
- PMID: 38762334
- PMCID: PMC11247960
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2024.04.009
Liquid-liquid phase separation in innate immunity
Abstract
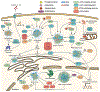
Intrinsic and innate immune responses are essential lines of defense in the body's constant surveillance of pathogens. The discovery of liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) as a key regulator of this primal response to infection brings an updated perspective to our understanding of cellular defense mechanisms. Here, we review the emerging multifaceted role of LLPS in diverse aspects of mammalian innate immunity, including DNA and RNA sensing and inflammasome activity. We discuss the intricate regulation of LLPS by post-translational modifications (PTMs), and the subversive tactics used by viruses to antagonize LLPS. This Review, therefore, underscores the significance of LLPS as a regulatory node that offers rapid and plastic control over host immune signaling, representing a promising target for future therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: DNA sensing; LLPS; PTMs; RNA sensing; immune signaling; innate immunity; membraneless organelles; phase separation; post-translational modification; proteomics; viral infection.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Shin Y. and Brangwynne CP (2017) Liquid phase condensation in cell physiology and disease. Science 357(6357):eaaf4382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

