Physical activity has decreased in Finnish children and adolescents from 2016 to 2022
- PMID: 38762462
- PMCID: PMC11102264
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-024-18854-7
Physical activity has decreased in Finnish children and adolescents from 2016 to 2022
Abstract
Background: Varying trends in children's and adolescents' physical activity (PA) have been reported during the last 10-20 years. Trends in sedentary behavior (SB) have been studied only rarely. The purpose of the present study was to describe population-based trends in accelerometer-measured PA, standing and SB, among Finnish 7-15-year-old children and adolescents, and to evaluate the potential influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on these behaviors.
Method: A cross-sectional population-based Finnish school-aged physical activity Study (FSPA) measured daily steps, vigorous (VPA), moderate (MPA), moderate-to-vigorous (MVPA), light physical activity (LPA), standing, and SB by an accelerometer for seven consecutive days in 2016, 2018, and 2022 (n = 7.080, 57% girls). The data was analyzed by multivariate regression analysis.
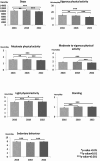
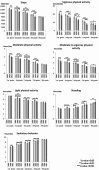
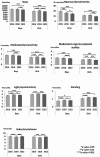
Results: In 2016, participants took on average 10.305 steps per day, and spent 0:15 (h: min) in VPA, 1:37 in MPA, 1:52 in MVPA, 3:48 in LPA, 0:55 in standing and 7:52 in SB. From 2016 to 2018, daily steps, MPA, LPA, and standing increased [229 steps (95% Confidence Interval, CI 70-387), 0:03 (CI 0:01 - 0:04), 0:11 (CI 0:09 - 0:14), and 0:07 (CI 0:05 - 0:08), respectively], while VPA and SB decreased [0:01 (CI 0:00-0:02) and 0:20 (CI 0:16 - 0:24), respectively]. From 2018 to 2022, daily PA and standing declined [751 steps (CI 562-939), VPA 0:02 (CI 0:01 - 0:03), MPA 0:09 (CI 0:07 - 0:11), MVPA 0:11 (CI 0:09 - 0:14), LPA 0:08 (CI 0:05 - 0:11), and standing 0:01 (CI 0:01 - 0:03)] while SB increased 0:21 (CI 0:16 - 0:25) indicating potential influence of the pandemic.
Conclusions: Children and adolescents became physically less active from 2016 to 2022. The potential effects of the COVID-19 were seen as declined PA and increased sedentariness from 2018 to 2022.
Keywords: Accelerometry; Physical activity; Sedentary behavior.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Carson V, Hunter S, Kuzik N, Gray CE, Poitras VJ, Chaput JP, Saunders TJ, Katzmarzyk PT, Okely AD, Connor Gorber S, et al. Systematic review of sedentary behaviour and health indicators in school-aged children and youth: an update. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2016;41(6 Suppl 3):S240–265. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2015-0630. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wu XY, Han LH, Zhang JH, Luo S, Hu JW, Sun K. The influence of physical activity, sedentary behavior on health-related quality of life among the general population of children and adolescents: a systematic review. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(11):e0187668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187668. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Poitras VJ, Gray CE, Borghese MM, Carson V, Chaput JP, Janssen I, Katzmarzyk PT, Pate RR, Connor Gorber S, Kho ME, et al. Systematic review of the relationships between objectively measured physical activity and health indicators in school-aged children and youth. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2016;41(6 Suppl 3):S197–239. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2015-0663. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 320400,320403 and 346607/the Strategic Research Council at the Academy of Finland
- 320400,320403 and 346607/the Strategic Research Council at the Academy of Finland
- 320400,320403 and 346607/the Strategic Research Council at the Academy of Finland
- 320400,320403 and 346607/the Strategic Research Council at the Academy of Finland
- 320400,320403 and 346607/the Strategic Research Council at the Academy of Finland
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

