Antiepileptic drug-loaded and multifunctional iron oxide@silica@gelatin nanoparticles for acid-triggered drug delivery
- PMID: 38762571
- PMCID: PMC11102556
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-62248-z
Antiepileptic drug-loaded and multifunctional iron oxide@silica@gelatin nanoparticles for acid-triggered drug delivery
Abstract
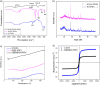
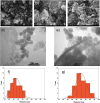
The current study developed an innovative design for the production of smart multifunctional core-double shell superparamagnetic nanoparticles (NPs) with a focus on the development of a pH-responsive drug delivery system tailored for the controlled release of Phenytoin, accompanied by real-time monitoring capabilities. In this regard, the ultra-small superparamagnetic iron oxide@silica NPs (IO@Si MNPs) were synthesized and then coated with a layer of gelatin containing Phenytoin as an antiepileptic drug. The precise saturation magnetization value for the resultant NPs was established at 26 emu g-1. The polymeric shell showed a pH-sensitive behavior with the capacity to regulate the release of encapsulated drug under neutral pH conditions, simultaneously, releasing more amount of the drug in a simulated tumorous-epileptic acidic condition. The NPs showed an average size of 41.04 nm, which is in the desired size range facilitating entry through the blood-brain barrier. The values of drug loading and encapsulation efficiency were determined to be 2.01 and 10.05%, respectively. Moreover, kinetic studies revealed a Fickian diffusion process of Phenytoin release, and diffusional exponent values based on the Korsmeyer-Peppas equation were achieved at pH 7.4 and pH 6.3. The synthesized NPs did not show any cytotoxicity. Consequently, this new design offers a faster release of PHT at the site of a tumor in response to a change in pH, which is essential to prevent epileptic attacks.
Keywords: Antiepileptic drug; Drug delivery; Gelatin; Phenytoin; Silica; Superparamagnetic nanoparticles; pH-sensitivity.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Phenytoin carried by silica core iron oxide nanoparticles reduces the expression of pharmacoresistant seizures in rats.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015;10(24):3563-77. doi: 10.2217/nnm.15.173. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26649451
-
Facile Layer-by-Layer Self-Assembly toward Enantiomeric Poly(lactide) Stereocomplex Coated Magnetite Nanocarrier for Highly Tunable Drug Deliveries.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016 Jan 27;8(3):1842-53. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b09822. Epub 2016 Jan 12. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016. PMID: 26717323
-
Magnetic targeting and pH-microwave dual responsive Janus mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug encapsulation and delivery.Nanotechnology. 2024 May 16;35(31). doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/ad42a3. Nanotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38657569
-
pH sensitive core-shell magnetic nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery in cancer therapy.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2016;57(1):23-32. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2016. PMID: 27151685 Review.
-
A review of DNA nanoparticles-encapsulated drug/gene/protein for advanced controlled drug release: Current status and future perspective over emerging therapy approaches.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 May;268(Pt 1):131694. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131694. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38642693 Review.
Cited by
-
Advancements in insulin delivery: the potential of natural polymers for improved diabetes management.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Apr 25;13:1566743. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1566743. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40352348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Overview of the Current Status and Advancements in Various Treatment Strategies against Epilepsy.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Nov 1;7(12):3729-3757. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00494. eCollection 2024 Dec 13. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39698272 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

