Tracing the origins of Plasmodium vivax resurgence after malaria elimination on Aneityum Island in Vanuatu
- PMID: 38762604
- PMCID: PMC11102431
- DOI: 10.1038/s43856-024-00524-9
Tracing the origins of Plasmodium vivax resurgence after malaria elimination on Aneityum Island in Vanuatu
Abstract
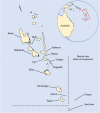
Background: Five years after successful malaria elimination, Aneityum Island in Vanuatu experienced an outbreak of Plasmodium vivax of unknown origin in 2002. Epidemiological investigations revealed several potential sources of P. vivax. We aimed to identify the genetic origin of P. vivax responsible for the resurgence.
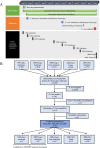
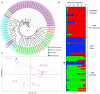
Methods: Five P. vivax microsatellite markers were genotyped using DNA extracted from archived blood samples. A total of 69 samples from four P. vivax populations was included: 29 from the outbreak in 2002, seven from Aneityum in 1999 and 2000, 18 from visitors to Aneityum in 2000, and 15 from nearby Tanna Island in 2002. A neighbour-joining phylogenetic tree was constructed to elucidate the relationships among P. vivax isolates. STRUCTURE and principal component analysis were used to assess patterns of genetic structure.
Results: Here we show distinct genetic origins of P. vivax during the outbreak on Aneityum. While the origin of most P. vivax lineages found during the outbreak remains unidentified, limited genetic diversity among these lineages is consistent with a rapid expansion from a recent common ancestor. Contemporaneous P. vivax from neighboring Tanna and potential relapse of P. vivax acquired from other islands in 1999 and 2000 are also identified as minor contributors to the outbreak.
Conclusions: Multiple reintroductions of P. vivax after elimination highlight the high receptivity and vulnerability to malaria resurgence in island settings of Vanuatu, despite robust surveillance and high community compliance to control measures.
Plain language summary
Plasmodium vivax is one of several parasite species that cause malaria. On Aneityum Island in Vanuatu, malaria had been eliminated in 1997, but an outbreak was reported in 2002 despite protective measures still being in place. Here, we analysed DNA of parasites from the outbreak to understand its origin, since parasites of different origins will have slight differences in their DNA. Most parasites had similar DNA suggesting they had a recent shared common ancestor whose origin remains unidentified. From this analysis we were also able to find a minority of parasites that likely came from Tanna in 2002, while another small group of parasites may have originated from parasites imported to Aneityum in 1999 or 2000. This illustrates the difficulty of maintaining a malaria-free status in resource-limited areas and the threat of imported malaria to elimination efforts.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. World Malaria Report 2022 (WHO, 2022).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

