Associations between genetic mutations in different SARS-CoV-2 strains and negative conversion time of viral RNA among imported cases in Hangzhou: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 38763300
- PMCID: PMC11137596
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2024.199400
Associations between genetic mutations in different SARS-CoV-2 strains and negative conversion time of viral RNA among imported cases in Hangzhou: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
Purpose: Previous studies on severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) have focused on factors that influence the achievement of negative conversion of viral RNA. This study aimed to investigate the effects of the genetic mutations in different SARS-CoV-2 strains on the negative conversion time (NCT) among imported cases in Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province, China, in order to provide valuable insights for developing targeted epidemic prevention guidelines.
Methods: This retrospective study involved 146 imported SARS-CoV-2 cases in Hangzhou from 8 April 2021 to 11 June 2022. We compared the SARS-CoV-2-specific indicators, clinical indexes, and NCT among the wild-type (WT), Delta, and Omicron groups. Spearman correlation analysis was used to identify the correlations of NCT with mutation types/frequencies.
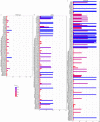
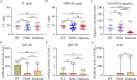
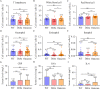
Results: The mean age of the imported cases was 35.3 (SD: 12.3) years, with 71.92 % males and 28.08 % females. The mean cycle threshold (Ct) values of open reading frame 1ab (ORF1ab) and nucleocapsid (N) RNA were 25.17 (SD: 6.44) and 23.4 (SD: 6.76), respectively. The mutations of SARS-CoV-2 strains were mainly located in N, membrane (M), spike (S), ORF1a, ORF1b, ORF3a, ORF6, and ORF9b genes among the WT, Delta, and Omicron groups. NCT was significantly prolonged in the WT and Delta groups compared to the Omicron group. T lymphocyte, white blood cell, eosinophil, and basophil counts were dramatically higher in the WT group than the Delta group. White blood cell, red blood cell, and basophil counts were significantly lower in the Delta group than the Omicron group. Spearman correlation analysis revealed a significant correlation between the NCT of viral RNA and mutation types of viral genes of WT and Omicron strains. Additionally, NCT was markedly negatively correlated with the frequencies of five mutations in Omicron strains (ORF1b:P1223L, ORF1b:R1315C, ORF1b:T2163I, ORF3a:T223I, and ORF6:D61L).
Conclusions: This study indicates that five mutations in Omicron strains (ORF1b:P1223L/R1315C/T2163I, ORF3a:T223I and ORF6:D61L) shortened NCT in imported SARS-CoV-2 cases.
Keywords: Genetic mutation; Imported cases; Negative conversion; SARS-CoV-2 strain.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epidemiological characteristics of 17 imported patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Mar 28;47(3):344-351. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2022.220040. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 35545327 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
[Genomic Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 Isolates Obtained from Antalya, Türkiye].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2024 Oct;58(4):433-447. doi: 10.5578/mb.20249643. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2024. PMID: 39745215 Turkish.
-
Clinical predictors and RT-PCR profile of prolonged viral shedding in patients with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant in Shanghai: A retrospective observational study.Front Public Health. 2022 Oct 24;10:1015811. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1015811. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36353283 Free PMC article.
-
Structural impact of a new spike Y170W mutation detected in early emerging SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants in France.Virus Res. 2024 May;343:199354. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2024.199354. Epub 2024 Mar 16. Virus Res. 2024. PMID: 38492859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral and antibody dynamics of acute infection with SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant (B.1.1.529): a prospective cohort study from Shenzhen, China.Lancet Microbe. 2023 Aug;4(8):e632-e641. doi: 10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00139-8. Epub 2023 Jul 14. Lancet Microbe. 2023. PMID: 37459867 Review.
References
-
- Aksamentov Ivan, Roemer Cornelius, Hodcroft E.B., et al. Nextclade: clade assignment, mutation calling and quality control for viral genomes. J. Open Source Softw. 2021;6:3773.
-
- Atluri V.L., Stalter R.M., McGuffin S.A., et al. Patient characteristics associated with conversion from negative to positive severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 polymerase chain reaction test results: implications for clinical false-negativity from a single-center: a case-control study. J. Med. Virol. 2022;94:4792–4802. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

