Multi-disciplinary strategy to optimize irrigation efficiency in irrigated agriculture
- PMID: 38763933
- PMCID: PMC11636869
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-61372-0
Multi-disciplinary strategy to optimize irrigation efficiency in irrigated agriculture
Abstract
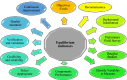
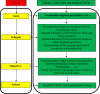
Equilibrium among water, food, energy, and climate actions is necessary for life to exist, quality, and sustainability. This article explored how to ensure sustainability, and equilibrium in the irrigation processes by proposing irrigation equilibrium indicators (IEIs) for sustainable irrigated agriculture (SIA). The primary purpose of IEIs is to achieve a state of sustainable climate and environmental balance. The pressures driving agriculture and irrigation professionals to enhance the irrigation scheme performance are tremendous in all agricultural communities. Monitoring, assessment, and improvement of agriculture practices and irrigation schemes for enhancing the Climate, water, food, and energy (CWFE) nexus is a must. As an auspicious climate action, IEIs were developed to enhance the irrigation scheme's efficiency, within the scope of SIA. Subsequently, water, agricultural, food, and energy productivity could be optimized. Then, the appropriate equilibrium indicators could identify the actual performance of the CWFE nexus as a whole and the performance of each component. The effective irrigation scheme is the backbone of SIA. IEIs could measure the degree of achieving the overall and specific objectives and designated irrigation processes. The ultimate measure of equilibrium is optimizing sustainable agricultural yields and productivity, ensuring environmental balance, strengthening life quality, and maximizing economic returns.
Keywords: Climate, water, food, and energy (CWFE) nexus; Efficiency; Global goals (GGs); Irrigation equilibrium indicators (IEIs); Sustainable irrigated agriculture (SIA); Water organizations.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Advancing irrigation management: integrating technology and sustainability to address global food security.Environ Monit Assess. 2024 Oct 5;196(11):1018. doi: 10.1007/s10661-024-13145-5. Environ Monit Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367142 Review.
-
Sustainable irrigation technologies: a water-energy-food (WEF) nexus perspective towards achieving more crop per drop per joule per hectare.Environ Res Lett. 2022 Jul 1;17(7):073003. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/ac7b39. Epub 2022 Jul 6. Environ Res Lett. 2022. PMID: 35812360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unravelling resources use efficiency and its drivers for water transfer and grain production processes in pumping irrigation system.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Apr 20;818:151810. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151810. Epub 2021 Nov 20. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 34813813
-
The water-energy-food-ecosystem nexus in the Danube River Basin: Exploring scenarios and implications of maize irrigation.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Mar 1;914:169405. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.169405. Epub 2023 Dec 19. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 38123083
-
The impact of irrigation modes on agricultural water-energy‑carbon nexus.Sci Total Environ. 2023 Feb 20;860:160493. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160493. Epub 2022 Nov 24. Sci Total Environ. 2023. PMID: 36435239
References
-
- Damerau, K., Waha, K. & Herrero, M. The impact of nutrient-rich food choices on agricultural water-use efficiency. Nat. Sustain.2, 233–241. 10.1038/s41893-019-0242-1 (2019).
-
- FAO. The State of the World’s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture—Systems at breaking point. Main report. Rome (2022). 10.4060/cb9910en
-
- Batisha, A. A lighthouse to future opportunities for sustainable water provided by intelligent water hackathons in the Arabsphere. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun.10, 675. 10.1057/s41599-023-02146-3 (2023).
-
- Abbasi, K. et al. Reducing the risks of nuclear war—the role of health professionals. Pediatr. Res.95, 585–586. 10.1038/s41390-023-02850-5 (2024).
-
- Ray, D. K. Even a small nuclear war threatens food security. Nat. Food3, 567–568. 10.1038/s43016-022-00575-y (2022). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

