MRIO: the Magnetic Resonance Imaging Acquisition and Analysis Ontology
- PMID: 38763990
- PMCID: PMC12080281
- DOI: 10.1007/s12021-024-09664-8
MRIO: the Magnetic Resonance Imaging Acquisition and Analysis Ontology
Abstract
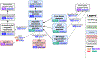
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is a useful tool in both the clinic and research settings, aiding in the diagnosis and treatments of neurological disease and expanding our knowledge of the brain. However, there are many challenges inherent in managing and analyzing MRI data, due in large part to the heterogeneity of data acquisition. To address this, we have developed MRIO, the Magnetic Resonance Imaging Acquisition and Analysis Ontology. MRIO provides well-reasoned classes and logical axioms for the acquisition of several MRI acquisition types and well-known, peer-reviewed analysis software, facilitating the use of MRI data. These classes provide a common language for the neuroimaging research process and help standardize the organization and analysis of MRI data for reproducible datasets. We also provide queries for automated assignment of analyses for given MRI types. MRIO aids researchers in managing neuroimaging studies by helping organize and annotate MRI data and integrating with existing standards such as Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine and the Brain Imaging Data Structure, enhancing reproducibility and interoperability. MRIO was constructed according to Open Biomedical Ontologies Foundry principles and has contributed several classes to the Ontology for Biomedical Investigations to help bridge neuroimaging data to other domains. MRIO addresses the need for a "common language" for MRI that can help manage the neuroimaging research, by enabling researchers to identify appropriate analyses for sets of scans and facilitating data organization and reporting.
Keywords: Biological Ontologies; Magnetic Resonance Imaging; Neuroimaging; Neuroinformatics; Translational Research, Biomedical.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors have no competing interests to report.
Figures





Update of
-
MRIO: The Magnetic Resonance Imaging Acquisition and Analysis Ontology.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 7:2023.08.04.552020. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.04.552020. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Neuroinformatics. 2024 Jul;22(3):269-283. doi: 10.1007/s12021-024-09664-8. PMID: 37609265 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
MRIO: The Magnetic Resonance Imaging Acquisition and Analysis Ontology.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 7:2023.08.04.552020. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.04.552020. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Neuroinformatics. 2024 Jul;22(3):269-283. doi: 10.1007/s12021-024-09664-8. PMID: 37609265 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Structural neuroimaging in psychosis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 May;12(18):iii-iv, ix-163. doi: 10.3310/hta12180. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18462577
-
Magnetic resonance perfusion for differentiating low-grade from high-grade gliomas at first presentation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 22;1(1):CD011551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011551.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29357120 Free PMC article.
-
Patient safety classifications, taxonomies and ontologies: A systematic review on development and evaluation methodologies.J Biomed Inform. 2022 Sep;133:104150. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2022.104150. Epub 2022 Jul 22. J Biomed Inform. 2022. PMID: 35878822
-
MRI software and cognitive fusion biopsies in people with suspected prostate cancer: a systematic review, network meta-analysis and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(61):1-310. doi: 10.3310/PLFG4210. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367754 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antoniou G, & Harmelen van. F (2009). Web ontology language: Owl. Handbook on ontologies, 91–110.
-
- Arp R (2015). Building ontologies with basic formal ontology / by Robert Arp, Barry Smith, and Andrew D. Spear. (Smith B & Spear AD, Eds.). Cambridge, Massachusetts: The MIT Press.
-
- Bartnik A, Smith M, & Dwyer M (2023). CBI Neuroinformatics Platform. https://gitlab.com/abartnik/cbi-project. Accessed 10 December 2023
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

