Combination of betulinic acid and EGFR-TKIs exerts synergistic anti-tumor effects against wild-type EGFR NSCLC by inducing autophagy-related cell death via EGFR signaling pathway
- PMID: 38764025
- PMCID: PMC11103851
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-024-02844-9
Combination of betulinic acid and EGFR-TKIs exerts synergistic anti-tumor effects against wild-type EGFR NSCLC by inducing autophagy-related cell death via EGFR signaling pathway
Erratum in
-
Correction: Combination of betulinic acid and EGFR‑TKIs exerts synergistic anti‑tumor effects against wild‑type EGFR NSCLC by inducing autophagy‑related cell death via EGFR signaling.Respir Res. 2025 Apr 13;26(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s12931-025-03223-8. Respir Res. 2025. PMID: 40223044 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have revolutionized the treatment of lung cancer patients with mutated EGFR. However, the efficacy of EGFR-TKIs in wild-type EGFR tumors has been shown to be marginal. Methods that can sensitize EGFR-TKIs to EGFR wild-type NSCLC remain rare. Hence, we determined whether combination treatment can maximize the therapeutic efficacy of EGFR-TKIs.
Methods: We established a focused drug screening system to investigate candidates for overcoming the intrinsic resistance of wild-type EGFR NSCLC to EGFR-TKIs. Molecular docking assays and western blotting were used to identify the binding mode and blocking effect of the candidate compounds. Proliferation assays, analyses of drug interactions, colony formation assays, flow cytometry and nude mice xenograft models were used to determine the effects and investigate the molecular mechanism of the combination treatment.
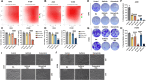
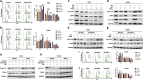
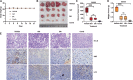
Results: Betulinic acid (BA) is effective at targeting EGFR and synergizes with EGFR-TKIs (gefitinib and osimertinib) preferentially against wild-type EGFR. BA showed inhibitory activity due to its interaction with the ATP-binding pocket of EGFR and dramatically enhanced the suppressive effects of EGFR-TKIs by blocking EGFR and modulating the EGFR-ATK-mTOR axis. Mechanistic studies revealed that the combination strategy activated EGFR-induced autophagic cell death and that the EGFR-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway was essential for completing autophagy and cell cycle arrest. Activation of the mTOR pathway or blockade of autophagy by specific chemical agents markedly attenuated the effect of cell cycle arrest. In vivo administration of the combination treatment caused marked tumor regression in the A549 xenografts.
Conclusions: BA is a potential wild-type EGFR inhibitor that plays a critical role in sensitizing EGFR-TKI activity. BA combined with an EGFR-TKI effectively suppressed the proliferation and survival of intrinsically resistant lung cancer cells via the inhibition of EGFR as well as the induction of autophagy-related cell death, indicating that BA combined with an EGFR-TKI may be a potential therapeutic strategy for overcoming the primary resistance of wild-type EGFR-positive lung cancers.
Keywords: Autophagic cell death; Betulinic acid; Cell cycle arrest; Combination therapy; EGFR-TKIs; Non-small cell lung cancer; Primary drug resistance; Wild-type EGFR.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Curcumin overcome primary gefitinib resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer cells through inducing autophagy-related cell death.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 13;38(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1234-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31196210 Free PMC article.
-
EZH2 inhibitors reverse resistance to gefitinib in primary EGFR wild-type lung cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2020 Dec 4;20(1):1189. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07667-7. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33276757 Free PMC article.
-
The HSP90 inhibitor ganetespib potentiates the antitumor activity of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibition in mutant and wild-type non-small cell lung cancer.Target Oncol. 2015 Jun;10(2):235-45. doi: 10.1007/s11523-014-0329-6. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Target Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25077897 Free PMC article.
-
A Structural Insight Into Two Important ErbB Receptors (EGFR and HER2) and Their Relevance to Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2025 Apr;358(4):e2400992. doi: 10.1002/ardp.202400992. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2025. PMID: 40194950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Silibinin Combined With EGFR-TKIs in the Treatment of NSCLC.Cancer Med. 2025 Feb;14(3):e70643. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70643. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 39907159 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Erdafitinib inhibits the tumorigenicity of MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer cells by inducing TRIM25/ubiquitin-dependent degradation of FGFR4.Breast Cancer Res. 2025 Jul 9;27(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s13058-025-02086-7. Breast Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40635078 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Pentacyclic Triterpenoids in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Potential.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Dec 26;17(1):22. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17010022. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39861671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correction: Combination of betulinic acid and EGFR‑TKIs exerts synergistic anti‑tumor effects against wild‑type EGFR NSCLC by inducing autophagy‑related cell death via EGFR signaling.Respir Res. 2025 Apr 13;26(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s12931-025-03223-8. Respir Res. 2025. PMID: 40223044 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The potential of targeting autophagy-related non-coding RNAs in the treatment of lung cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 14;16:1551258. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1551258. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40438586 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Herbst R, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature. 2018;553:446–54. - PubMed
-
- To C, Beyett T, Jang J, Fang WW, Bahcall M, Haikala HM, Shin BH, Heppner DE, Rana JK, Leeper BA, Soroko KM, Poitras MJ, Gokhale PC, Kobayashi Y, Wahid K, Kurppa KJ, Gero TW, Cameron MD, Ogino A, Mushajiang M, Xu C, Zhang Y, Scott DA, Eck MJ, Gray NS, Jänne PA. Allosteric inhibition of drug resistant forms of EGFR L858R mutant NSCLC. Nat Cancer. 2022;3:402–17. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

