Effect of baicalin on eradicating biofilms of bovine milk derived Acinetobacter lwoffii
- PMID: 38764041
- PMCID: PMC11103975
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-024-04015-w
Effect of baicalin on eradicating biofilms of bovine milk derived Acinetobacter lwoffii
Abstract
Background: Acinetobacter lwoffii (A.lwoffii) is a serious zoonotic pathogen that has been identified as a cause of infections such as meningitis, bacteremia and pneumonia. In recent years, the infection rate and detection rate of A.lwoffii is increasing, especially in the breeding industry. Due to the presence of biofilms, it is difficult to eradicate and has become a potential super drug-resistant bacteria. Therefore, eradication of preformed biofilm is an alternative therapeutic action to control A.lwoffii infection. The present study aimed to clarify that baicalin could eradicate A.lwoffii biofilm in dairy cows, and to explore the mechanism of baicalin eradicating A.lwoffii.
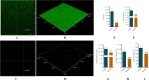
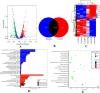
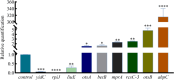
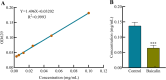
Results: The results showed that compared to the control group, the 4 MIC of baicalin significantly eradicated the preformed biofilm, and the effect was stable at this concentration, the number of viable bacteria in the biofilm was decreased by 0.67 Log10CFU/mL. The total fluorescence intensity of biofilm bacteria decreased significantly, with a reduction rate of 67.0%. There were 833 differentially expressed genes (367 up-regulated and 466 down-regulated), whose functions mainly focused on oxidative phosphorylation, biofilm regulation system and trehalose synthesis. Molecular docking analysis predicted 11 groups of target proteins that were well combined with baicalin, and the content of trehalose decreased significantly after the biofilm of A.lwoffii was treated with baicalin.
Conclusions: The present study evaluated the antibiofilm potential of baicalin against A.lwoffii. Baicalin revealed strong antibiofilm potential against A.lwoffii. Baicalin induced biofilm eradication may be related to oxidative phosphorylation and TCSs. Moreover, the decrease of trehalose content may be related to biofilm eradication.
Keywords: Acinetobacter lwoffii; Baicalin; Biofilm; Eradication; Trehalose.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
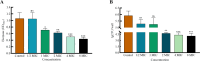
Similar articles
-
Four novel Acinetobacter lwoffii strains isolated from the milk of cows in China with subclinical mastitis.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Jun 26;20(1):274. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04119-3. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38918815 Free PMC article.
-
Differential development of antibiotic resistance and virulence between Acinetobacter species.mSphere. 2024 May 29;9(5):e0010924. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00109-24. Epub 2024 Apr 5. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 38578105 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of secondary metabolite of Actinidia deliciosa on the biofilm and extra-cellular matrix components of Acinetobacter baumannii.Microb Pathog. 2017 Sep;110:345-351. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.07.013. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Microb Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28705748
-
Hybrid combinations containing natural products and antimicrobial drugs that interfere with bacterial and fungal biofilms.Phytomedicine. 2017 Dec 15;37:14-26. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2017.10.021. Epub 2017 Nov 23. Phytomedicine. 2017. PMID: 29174600 Review.
-
Evolving biofilm inhibition and eradication in clinical settings through plant-based antibiofilm agents.Phytomedicine. 2023 Oct;119:154973. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154973. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37499434 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural Products for Improving Soft Tissue Healing: Mechanisms, Innovations, and Clinical Potential.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jun 8;17(6):758. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17060758. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40574070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of anti-biofilm peptide CRAMP-34 on the biofilms of Acinetobacter lwoffii derived from dairy cows.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Aug 15;14:1406429. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1406429. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39211795 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights in Natural Bioactive Compounds for Periodontal Disease: Advanced Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential.Molecules. 2025 Feb 10;30(4):807. doi: 10.3390/molecules30040807. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40005119 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Avery TM, Boone RL, Lu J, Spicer SK, Guevara MA, Moore RE, Chambers SA, Manning SD, Dent L, Marshall D, et al. Analysis of Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activity of Human Milk Lactoferrin Compared to Bovine Lactoferrin against Multidrug Resistant and Susceptible Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates. ACS Infect Dis. 2021;7:2116–2126. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00087. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 202310635087/National Training Program of Innovation and Entrepreneurship for Undergraduates
- SWU-KQ22045/Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities
- CSTB2023TIAD-LDX0006/Chongqing Technical Innovation and Application Development Special General Project
- NCTIP-XD/B12, NCTIP-XD/C17/National Center of Technology Innovation for Pigs
- 022LYXZ030/the Project of Shandong Province on the Transformation of Scientific and Technological Achievements
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

