Correlation between small-cell lung cancer serum protein/peptides determined by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry and chemotherapy efficacy
- PMID: 38764042
- PMCID: PMC11103996
- DOI: 10.1186/s12014-024-09483-8
Correlation between small-cell lung cancer serum protein/peptides determined by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry and chemotherapy efficacy
Abstract
Background: Currently, no effective measures are available to predict the curative efficacy of small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) chemotherapy. We expect to develop a method for effectively predicting the SCLC chemotherapy efficacy and prognosis in clinical practice in order to offer more pertinent therapeutic protocols for individual patients.
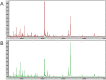
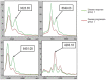
Methods: We adopted matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS) and ClinPro Tools system to detect serum samples from 154 SCLC patients with different curative efficacy of standard chemotherapy and analyze the different peptides/proteins of SCLC patients to discover predictive tumor markers related to chemotherapy efficacy. Ten peptide/protein peaks were significantly different in the two groups.
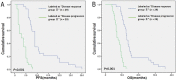
Results: A genetic algorithm model consisting of four peptides/proteins was developed from the training group to separate patients with different chemotherapy efficacies. Among them, three peptides/proteins (m/z 3323.35, 6649.03 and 6451.08) showed high expression in the disease progression group, whereas the peptide/protein at m/z 4283.18 was highly expressed in the disease response group. The classifier exhibited an accuracy of 91.4% (53/58) in the validation group. The survival analysis showed that the median progression-free survival (PFS) of 30 SCLC patients in disease response group was 9.0 months; in 28 cases in disease progression group, the median PFS was 3.0 months, a statistically significant difference (χ2 = 46.98, P < 0.001). The median overall survival (OS) of the two groups was 13.0 months and 7.0 months, a statistically significant difference (χ2 = 40.64, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: These peptides/proteins may be used as potential biological markers for prediction of the curative efficacy and prognosis for SCLC patients treated with standard regimen chemotherapy.
Keywords: Chemotherapy; Matrix assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight-mass spectrometry; Prediction of efficacy; Proteomics; Small-cell lung cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Detection of Serum Peptides in Patients with Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma by MALDI-TOF-MS and Analysis of Their Correlation with Chemotherapy Efficacy].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2017 May 20;20(5):318-325. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2017.05.04. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28532539 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Support vector machines coupled with proteomics approaches for detecting biomarkers predicting chemotherapy resistance in small cell lung cancer.Oncol Rep. 2012 Dec;28(6):2233-8. doi: 10.3892/or.2012.2037. Epub 2012 Sep 17. Oncol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22992788
-
Classification of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene Mutation Status Using Serum Proteomic Profiling Predicts Tumor Response in Patients with Stage IIIB or IV Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 5;10(6):e0128970. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128970. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26047516 Free PMC article.
-
Current Status of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization-Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) in Clinical Diagnostic Microbiology.Molecules. 2020 Oct 17;25(20):4775. doi: 10.3390/molecules25204775. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33080897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomaterials as Assisted Matrix of Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry for the Analysis of Small Molecules.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2017 Apr 21;7(4):87. doi: 10.3390/nano7040087. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28430138 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights.Open Life Sci. 2025 Jul 18;20(1):20251136. doi: 10.1515/biol-2025-1136. eCollection 2025. Open Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40688408 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cheng S, Evans WK, Stys-Norman D, Shepherd FA, Lung Cancer Disease Site Group of Cancer Care Ontario’s program in evidence-based C. Chemotherapy for relapsed small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and practice guideline. J Thorac Oncology: Official Publication Int Association Study Lung Cancer. 2007;2(4):348–54. doi: 10.1097/01.JTO.0000263720.15062.51. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
