Impact of Privatization on Healthcare System: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 38764559
- PMCID: PMC11098275
- DOI: 10.4103/sjmms.sjmms_510_23
Impact of Privatization on Healthcare System: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: A notable shift in healthcare policy is healthcare privatization, which refers to the transfer of ownership, management, or provision of healthcare services from the public sector to private entities.
Objectives: To provide a narrative examination of the impact of privatization on various dimensions of healthcare, including quality, equity, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. Policymakers can utilize the findings of this study to make well-informed decisions regarding privatization strategies.
Materials and methods: A systematic review was implemented using the following databases: PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar. Studies conducted from January 2000 to January 2023 in developing or developed countries that assessed the impact of healthcare privatization on population health within public sector institutions were included.
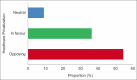
Results: Eleven studies were included. The findings revealed diverse perspectives on the impact of healthcare privatization, with four studies (36.4%) supporting privatization (two of these were conducted in Saudi Arabia), six studies (54.5%) opposing it (three of these were conducted in European countries), and one study (9.1%) taking a neutral stance. Two studies investigated the impact on healthcare quality, and both revealed that privatization negatively impacts uninsured patients and low-income populations. In addition, five studies investigated the healthcare access and equity dimensions following privatization: one was in favor, one was neutral, and three were opposing it. Four studies investigated the cost-effectiveness dimension, with three in favor and one study opposing it.
Conclusion: This review highlights different perspectives on healthcare privatization. While studies, as those from Saudi Arabia, suggest benefits in terms of efficiency and innovation, others, particularly from European countries, emphasize negative consequences such as inequity and reduced quality. This emphasizes the need for more investigations to understand privatization's impact on healthcare.
Keywords: Access to care; healthcare; healthcare delivery; impact; private sector; privatization; quality of health care; system.
Copyright: © 2024 Saudi Journal of Medicine & Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Saltman RB, Durán A, Dubois HF. Governing public hospitals: Reform strategies and the movement towards institutional autonomy. [[Last accessed 2023 Sept 24]];Health Policy. 2019 123:827–32. Available from: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/326425 .
-
- Levi B, Zehavi A. Religious and ethnic identities influence on public views of privatization: The case of Israel. Policy Stud. 2023;44:236–57.
-
- Duggan M, Gupta A, Jackson E, Templeton ZS. The Impact of Privatization: Evidence from the Hospital Sector. Cambridge, MA: National Bureau of Economic Research; 2023.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources