The deregulation of arachidonic acid metabolism in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 38764576
- PMCID: PMC11100328
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1381894
The deregulation of arachidonic acid metabolism in ovarian cancer
Abstract
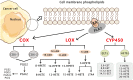
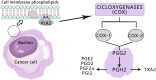
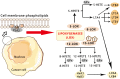
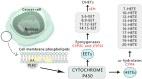
Arachidonic acid (AA) is a crucial polyunsaturated fatty acid in the human body, metabolized through the pathways of COX, LOX, and cytochrome P450 oxidase to generate various metabolites. Recent studies have indicated that AA and its metabolites play significant regulatory roles in the onset and progression of ovarian cancer. This article examines the recent research advancements on the correlation between AA metabolites and ovarian cancer, both domestically and internationally, suggesting their potential use as biological markers for early diagnosis, targeted therapy, and prognosis monitoring.
Keywords: arachidonic acid; biological marker; metabolic pathway; ovarian cancer; targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2024 Xia, Gao, Yang, Xing and Ji.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

