Extracellular vesicles in non-small cell lung cancer stemness and clinical applications
- PMID: 38765006
- PMCID: PMC11099288
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1369356
Extracellular vesicles in non-small cell lung cancer stemness and clinical applications
Abstract
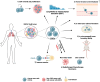
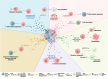
Non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) accounts for 85% of lung cancers, the leading cause of cancer associated deaths in the US and worldwide. Within NSCLC tumors, there is a subpopulation of cancer cells termed cancer stem cells (CSCs) which exhibit stem-like properties that drive NSCLC progression, metastasis, relapse, and therapeutic resistance. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are membrane-bound nanoparticles secreted by cells that carry vital messages for short- and long-range intercellular communication. Numerous studies have implicated NSCLC CSC-derived EVs in the factors associated with NSCLC lethality. In this review, we have discussed mechanisms of EV-directed cross-talk between CSCs and cells of the tumor microenvironment that promote stemness, tumor progression and metastasis in NSCLC. The mechanistic studies discussed herein have provided insights for developing novel NSCLC diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers and strategies to therapeutically target the NSCLC CSC niche.
Keywords: biomarkers; cancer stem cells; extracellular vesicles; metastasis; non-small cell lung cancer; oncogenic signaling; therapeutic targeting; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2024 Pandya, Al-Qasrawi, Klinge and Justilien.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel pathway for stemness propagation and chemoresistance in non-small cell lung cancer via phosphorylated PKM2-loaded small extracellular vesicles.Theranostics. 2025 Feb 24;15(8):3439-3461. doi: 10.7150/thno.103722. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40093893 Free PMC article.
-
RAB27B Drives a Cancer Stem Cell Phenotype in NSCLC Cells Through Enhanced Extracellular Vesicle Secretion.Cancer Res Commun. 2023 Apr 17;3(4):607-620. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-22-0425. eCollection 2023 Apr. Cancer Res Commun. 2023. PMID: 37077938 Free PMC article.
-
IL-10 derived from M2 macrophage promotes cancer stemness via JAK1/STAT1/NF-κB/Notch1 pathway in non-small cell lung cancer.Int J Cancer. 2019 Aug 15;145(4):1099-1110. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32151. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Int J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30671927
-
Small extracellular vesicles: Multi-functional aspects in non-small cell lung carcinoma.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2024 Jun;198:104341. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2024.104341. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38575042 Review.
-
Unraveling the Connection: Extracellular Vesicles and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Aug 9;19:8139-8157. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S477851. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39139506 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Salivary Extracellular Vesicles in Detection of Cancers Other than Head and Neck: A Systematic Review.Cells. 2025 Mar 11;14(6):411. doi: 10.3390/cells14060411. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40136660 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

