Therapeutic implications of quercetin and its derived-products in COVID-19 protection and prophylactic
- PMID: 38765079
- PMCID: PMC11098804
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30080
Therapeutic implications of quercetin and its derived-products in COVID-19 protection and prophylactic
Abstract
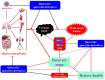
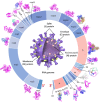
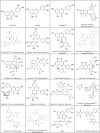
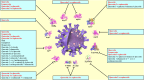
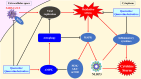
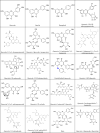
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), a novel human coronavirus, which has triggered a global pandemic of the coronavirus infectious disease 2019 (COVID-19). Outbreaks of emerging infectious diseases continue to challenge human health worldwide. The virus conquers human cells through the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor-driven pathway by mostly targeting the human respiratory tract. Quercetin is a natural flavonoid widely represented in the plant kingdom. Cumulative evidence has demonstrated that quercetin and its derivatives have various pharmacological properties including anti-cancer, anti-hypertension, anti-hyperlipidemia, anti-hyperglycemia, anti-microbial, antiviral, neuroprotective, and cardio-protective effects, because it is a potential treatment for severe inflammation and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Furthermore, it is the main life-threatening condition in patients with COVID-19. This article provides a comprehensive review of the primary literature on the predictable effectiveness of quercetin and its derivatives docked to multi-target of SARS-CoV-2 and host cells via in silico and some of validation through in vitro, in vivo, and clinically to fight SARS-CoV-2 infections, contribute to the reduction of inflammation, which suggests the preventive and therapeutic latency of quercetin and its derived-products against COVID-19 pandemic, multisystem inflammatory syndromes (MIS), and long-COVID.
Keywords: COVID-19; In silico; Long-COVID; MIS; Quercetin.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Kawasumi T., Takeno S., Ishino T., et al. Co-Expression and localization of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) and the transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2) in paranasal ciliated epithelium of patients with chronic Rhinosinusitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy36. 2022;(3):313–322. doi: 10.1177/19458924211059639. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

