A novel microRNA miR-4433a-3p as a potential diagnostic biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 38765119
- PMCID: PMC11101798
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30646
A novel microRNA miR-4433a-3p as a potential diagnostic biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Lung adenocarcinoma is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths because of the lack of early specific clinical indicators. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have become the focus in lung cancer diagnosis. Further studies are required to explore miRNA expression in the serum of lung adenocarcinoma patients and their correlation with therapy and analyse specific messenger RNA targets to improve the specificity and sensitivity of early diagnosis.
Methods: The Toray 3D-Gene miRNA array was used to compare the expression levels of various miRNAs in the sera of patients with lung adenocarcinoma and healthy volunteers. Highly expressed miRNAs were selected for further analysis. To verify the screening results, serum and pleural fluid samples were analysed using qRT-PCR. Serum levels of the miRNAs and their correlation with the clinical information of patients with lung adenocarcinoma were analysed. The functions of miRNAs were further analysed using the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Gene and Genomes and Gene Ontology databases.
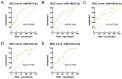
Results: Microarray analysis identified 60 and 50 miRNAs with upregulated and downregulated expressions, respectively, in the serum of patients with lung adenocarcinoma compared to those in healthy individuals. Using qRT-qPCR to detection of miRNAs expression in the serum or pleural effusion of patients with early and advanced lung adenocarcinoma, we found that miR-4433a-3p could be used as a diagnostic marker and therapeutic evaluation indicator for lung adenocarcinoma. Serum of miR-4433a-3p levels significantly correlated with the clinical stage. miR-4433a-3p may be more suitable than other tumour markers for the early diagnosis and evaluation of therapeutic effects in lung adenocarcinoma. miR-4433a-3p may affect tumour growth and metastasis by acting on target genes (PIK3CD, UBE2J2, ICMT, PRDM16 and others) and regulating tumour-related signalling pathways (MAPK signal pathway, Ras signalling pathway and others).
Conclusion: miR-4433a-3p may serve as a biomarker for the early diagnosis of lung adenocarcinoma and monitoring of therapeutic effects.
Keywords: Biomarker; Early diagnosis; Lung adenocarcinoma; Treatment; microRNAs.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests:Zhongxiang Liu reports financial support was provided by the Elderly Health Research Project of 10.13039/501100002949Jiangsu Province. Zhongxiang Liu has patent pending to Guan Sun. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures









References
-
- Howington J.A., Blum M.G., Chang A.C., Balekian A.A., Murthy S.C. Treatment of stage I and II non-small cell lung cancer: diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2013;143:e278S–e313S. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2359. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Musika W., Kamsa-Ard S., Jirapornkul C., Santong C., Phunmanee A. Lung cancer survival with current therapies and new targeted treatments: a comprehensive update from the srinagarind hospital-based cancer registry from (2013 to 2017) Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP. 2021;22:2501–2507. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.8.2501. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

