Anticoagulation Management Post Pulmonary Embolism
- PMID: 38765210
- PMCID: PMC11100539
- DOI: 10.14797/mdcvj.1338
Anticoagulation Management Post Pulmonary Embolism
Abstract
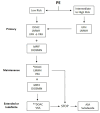
Pulmonary embolus (PE) carries a significant impending morbidity and mortality, especially in intermediate and high-risk patients, and the choice of initial anticoagulation that allows for therapeutic adjustment or manipulation is important. The preferred choice of anticoagulation management includes direct oral anticoagulants. Vitamin K antagonists and low-molecular-weight heparin are preferred in special populations or selected patients such as breastfeeding mothers, those with end-stage renal disease, or obese patients, among others. This article reviews the primary and longer-term considerations for anticoagulation management in patients with PE and highlights special patient populations and risk factor considerations.
Keywords: anticoagulation; deep vein thrombosis; direct oral anticoagulants; low molecular weight heparin; pulmonary embolus; revascularization; unfractionated heparin; venotonics; venous thromboembolism.
Copyright: © 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author has no competing interests to declare.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

