Oxya chinensis sinuosa (OC) Extracts Protects ARPE-19 Cells against Oxidative Stress via Activation of the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases (MAPKs)/ Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB) Pathway
- PMID: 38765280
- PMCID: PMC11097018
- DOI: 10.5851/kosfa.2024.e15
Oxya chinensis sinuosa (OC) Extracts Protects ARPE-19 Cells against Oxidative Stress via Activation of the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases (MAPKs)/ Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB) Pathway
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Oxya chinensis sinuosa (OC) Extracts Protects ARPE-19 Cells against Oxidative Stress via Activation of the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases (MAPKs)/Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB) Pathway.Food Sci Anim Resour. 2024 Jul;44(4):966. doi: 10.5851/kosfa.2024.e48. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Food Sci Anim Resour. 2024. PMID: 38974731 Free PMC article.
Abstract
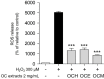
Oxya chinensis sinuosa (OC) is a well-known edible insect. Several researches on the health benefits of OC consumption have been performed to date; however, their effect on eye health remains largely unknown. This study aimed to assess the protective effects of OC extracts on the oxidative stress on the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells. Oxidative damage has been identified as one of the key regulatory factors in age-related macular degeneration. H2O2-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, a well-known oxidative stress factor, can cause cell death in retinal pigment epithelia cells. In this study, we found that three OC extracts effectively prevented H2O2-induced ROS production and subsequent death of ARPE-19 cells in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, the OC extracts inhibited the phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases including p38, JNK, and ERK. The OC extracts restored IκBα degradation induced by H2O2, indicating that OC extracts suppressed the activation of nuclear factor-κB. Furthermore, the three OC extracts were shown to have antioxidant effects by up-regulating the intracellular expression of key antioxidant proteins such as SOD, NQO, and HO-1. Here we demonstrated the antioxidant and anti-apoptotic effects of the OC extracts on ARPE-19, indicating their potential role in improving eye health. These results suggest that three OC extracts plays a critical role in oxidative stress-induced cell death protects in ARPE-19 cells.
Keywords: Oxya chinensis sinuosa; age-related macular degeneration; antioxidant; edible insect; eye health functional food.
© Korean Society for Food Science of Animal Resources.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Anusha S, Negi PS. Edible insects and gut health. In: Bagchi D, Ohia SE, editors. Nutrition and functional foods in boosting digestion, metabolism and immune health. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2022. pp. 523–539. (ed) - DOI
-
- Bahuguna A, Khaket TP, Bajpai VK, Shukla S, Park I, Na M, Huh YS, Han YK, Kang SC, Kim M. N-acetyldopamine dimers from Oxya chinensis sinuosa attenuates lipopolysaccharides induced inflammation and inhibits cathepsin C activity. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022;20:1177–1188. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.02.011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bukkens SGF. The nutritional value of edible insects. Ecol Food Nutr. 1997;36:287–319. doi: 10.1080/03670244.1997.9991521. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

