Co-infectious Uveitis With Syphilis and Lyme Disease: A Case Report
- PMID: 38765401
- PMCID: PMC11102814
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.58608
Co-infectious Uveitis With Syphilis and Lyme Disease: A Case Report
Abstract
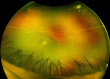
Uveitis is the inflammation of the uveal tract (i.e., iris, ciliary body, and choroid). Uveitis is categorized into the following three types based on the anatomical location of inflammation: anterior, intermediate, and posterior uveitis. Severe cases may lead to panuveitis, where all three layers may become inflamed potentially resulting in permanent vision loss. Uveitis can arise from different underlying disorders, including infectious causes or autoimmune disorders. Syphilis and Lyme disease are uncommon causes of uveitis. Eye involvement can occur at any stage in Lyme disease, characterized by diverse manifestations such as conjunctivitis, episcleritis, keratitis, uveitis, neuroretinitis, and retinal vasculitis. Patients may present with symptoms of blurred vision, eye pain or discomfort, visual floaters, headache, or intolerance to light. Patients can risk vision loss if not diagnosed and treated promptly.
Keywords: blindness; eye pain; lyme disease; ocular syphilis; uveitis.
Copyright © 2024, Mandal et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Lyme disease-associated uveitis: a case report and review emphasizing the importance of travel history and geographic considerations. [ Aug; 2023 ]. 2023. https://morancore.utah.edu/section-09-intraocular-inflammation-and-uveit... https://morancore.utah.edu/section-09-intraocular-inflammation-and-uveit...
-
- A case of Lyme disease accompanied by uveitis and white dot syndrome. Kılıç Müftüoğlu İ, Aydın Akova Y, Gür Güngör S. https://doi.org/10.4274/tjo.25991. Turk J Ophthalmol. 2016;46:241–243. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources