A Case of Acromegaly With Progressed Diabetic Retinopathy and Sarcopenia Diagnosed Following the Onset of Severe Hypoglycemia
- PMID: 38765413
- PMCID: PMC11100447
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.58461
A Case of Acromegaly With Progressed Diabetic Retinopathy and Sarcopenia Diagnosed Following the Onset of Severe Hypoglycemia
Abstract
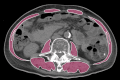
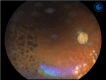
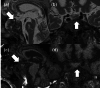
Acromegaly is a rare disorder characterized by excessive production of growth hormone (GH) from a pituitary tumor, typically leading to elevated glucose levels due to increased insulin resistance; hypoglycemia is rare. However, the long-term effect of excess GH on the peripheral organs is still unclear. Here we present a 69-year-old man evaluated for the cause of a hypoglycemic episode. He was underweight (body mass index: 17.3 kg/m2) with sarcopenia, which potentially contributed to his hypoglycemia. Notably, he exhibited progressed proliferative diabetic retinopathy compared to other microvascular complications, leading to further endocrinological investigation. As a result, he was diagnosed with acromegaly showing elevated GH and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) with a pituitary tumor. Opting against transsphenoidal surgery (TSS), the patient was treated with a somatostatin analog (SSA), achieving normalized IGF-1 levels with a monthly 120 mg lanreotide injection. In this case, acromegaly could lead to sarcopenia from GH-derived gluconeogenesis in the peripheral organs such as the reduction of muscle leading to reduced glucose reserves. Acromegaly in the elderly may present atypicality. Clinicians should be vigilant for unique manifestations such as advanced diabetic retinopathy, even in elderly patients with hypoglycemia.
Keywords: acromegaly; diabetic retinopathy; hypoglycemia; insulin autoimmune disease; sarcopenia.
Copyright © 2024, Kubo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- A consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of acromegaly comorbidities: an update. Giustina A, Barkan A, Beckers A, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105:0–46. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
