Integrated Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation Approach to Investigate the Mechanisms of Radix Rehmanniae Praeparata - Angelica Sinensis - Radix Achyranthis Bidentatae in Treating Knee Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 38765877
- PMCID: PMC11102756
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S455006
Integrated Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation Approach to Investigate the Mechanisms of Radix Rehmanniae Praeparata - Angelica Sinensis - Radix Achyranthis Bidentatae in Treating Knee Osteoarthritis
Abstract
Background: Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is a persistent degenerative condition characterized by the deterioration of cartilage. The Chinese herbal formula Radix Rehmanniae Praeparata- Angelica Sinensis-Radix Achyranthis Bidentatae (RAR) has often been used in effective prescriptions for KOA as the main functional drug, but its underlying mechanism remains unclear. Therefore, network pharmacology and verification experiments were employed to investigate the impact and mode of action of RAR in the treatment of KOA.
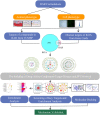
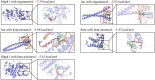
Methods: The destabilization of the medial meniscus model (DMM) was utilized to assess the anti-KOA effect of RAR by using gait analysis, micro-computed tomography (Micro-CT), and histology. Primary chondrocytes were extracted from the rib cartilage of a newborn mouse. The protective effects of RAR on OA cells were evaluated using a CCK-8 assay. The antioxidative effect of RAR was determined by measuring reactive oxygen species (ROS), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione (GSH) production. Furthermore, network pharmacology and molecular docking were utilized to propose possible RAR targets for KOA, which were further verified through experiments.
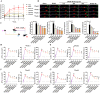
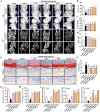
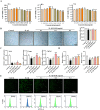
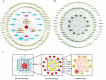
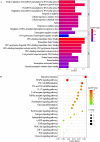
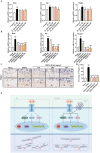
Results: In vivo, RAR significantly ameliorated DMM-induced KOA characteristics, such as subchondral bone sclerosis, cartilage deterioration, gait abnormalities, and the degree of knee swelling. In vitro, RAR stimulated chondrocyte proliferation and the expression of Col2a1, Comp, and Acan. Moreover, RAR treatment significantly reduced ROS accumulation in an OA cell model induced by IL-1β and increased the activity of antioxidant enzymes (SOD and GSH). Network pharmacology analysis combined with molecular docking showed that Mapk1 might be a key therapeutic target. Subsequent research showed that RAR could downregulate Mapk1 mRNA levels in IL-1β-induced chondrocytes and DMM-induced rats.
Conclusion: RAR inhibited extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation and oxidative stress response via the MAPK signaling pathway in KOA, and Mapk1 may be a core target.
Keywords: Mapk1; RAR; cartilage degeneration; knee osteoarthritis; network pharmacology.
© 2024 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

