This is a preprint.
Structural basis for Rab6 activation by the Ric1-Rgp1 complex
- PMID: 38766083
- PMCID: PMC11100747
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.05.06.592747
Structural basis for Rab6 activation by the Ric1-Rgp1 complex
Update in
-
Structural basis for Rab6 activation by the Ric1-Rgp1 complex.Nat Commun. 2024 Dec 4;15(1):10561. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54869-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39632878 Free PMC article.
Abstract
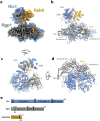
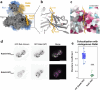
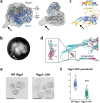
Rab GTPases act as molecular switches to regulate organelle homeostasis and membrane trafficking. Rab6 plays a central role in regulating cargo flux through the Golgi and is activated via nucleotide exchange by the Ric1-Rgp1 protein complex. Ric1-Rgp1 is conserved throughout eukaryotes but the structural and mechanistic basis for its function has not been established. Here we report the cryoEM structure of a Ric1-Rgp1-Rab6 complex representing a key intermediate of the nucleotide exchange reaction. This structure reveals the overall architecture of the complex and enabled us to identify interactions critical for proper recognition and activation of Rab6 on the Golgi membrane surface. Ric1-Rgp1 interacts with the nucleotide-binding domain of Rab6 using an uncharacterized helical domain, which we establish as a novel RabGEF domain by identifying residues required for Rab6 nucleotide exchange. Unexpectedly, the complex uses an arrestin fold to interact with the Rab6 hypervariable domain, indicating that interactions with the unstructured C-terminal regions of Rab GTPases may be a common specificity mechanism used by their activators. Collectively, our findings provide a detailed mechanistic understanding of regulated Rab6 activation at the Golgi.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
