This is a preprint.
Effects of parity and early pregnancy on peripheral blood leukocytes in dairy cattle
- PMID: 38766084
- PMCID: PMC11100682
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.05.06.592827
Effects of parity and early pregnancy on peripheral blood leukocytes in dairy cattle
Update in
-
Effects of parity and early pregnancy on peripheral blood leukocytes in dairy cattle.J Dairy Sci. 2024 Dec;107(12):11728-11743. doi: 10.3168/jds.2024-25063. Epub 2024 Aug 30. J Dairy Sci. 2024. PMID: 39216517
Abstract
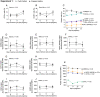
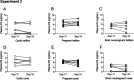
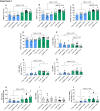
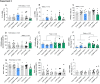
Subfertility remains a major problem in the dairy industry. Only 35-40% of high-yielding dairy cows and 55-65% of nonlactating heifers become pregnant after their first service. The immune system plays a critical role in the establishment of pregnancy. However, it can also create challenges for embryo survival and contribute to reduced fertility. We conducted 2 separate experiments to characterize changes in subsets of peripheral blood leukocytes (PBL) and their phenotype over the estrous cycle and early pregnancy in heifers and cows. We used flow cytometry and RT-qPCR to assess protein and mRNA expression of molecules important for immune function. We observed that monocytes and T cells were most affected by pregnancy status in heifers, whereas, CD8+ lymphocytes and natural killer (NK) cells were most affected during early pregnancy in cows. Changes in immune parameters measured appeared to be greater in heifers than cows including changes in expression of numerous immune function molecules. To test the hypothesis, we conducted a third experiment to simultaneously analyze the immunological responses to pregnancy between cows and heifers. We observed that cows had greater expression of proinflammatory cytokines and molecules associated with leukocyte migration and phagocytosis compared to heifers. Moreover, animals that failed to become pregnant showed altered expression of anti-inflammatory molecules. Overall, these findings support the hypothesis that early pregnancy signaling alters the proportions and functions of peripheral blood immune cells and differences between cows and heifers may yield insight into the reduced fertility of mature lactating dairy cows.
Keywords: bovine; cytokines; immune; leukocytes; pregnancy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of parity and early pregnancy on peripheral blood leukocytes in dairy cattle.J Dairy Sci. 2024 Dec;107(12):11728-11743. doi: 10.3168/jds.2024-25063. Epub 2024 Aug 30. J Dairy Sci. 2024. PMID: 39216517
-
mRNA of luteal genes associated with progesterone synthesis, maintenance, and apoptosis in dairy heifers and lactating dairy cows.Anim Reprod Sci. 2010 Sep;121(3-4):218-24. doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2010.05.016. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Anim Reprod Sci. 2010. PMID: 20599333
-
Effects of early pregnancy on uterine lymphocytes and endometrial expression of immune-regulatory molecules in dairy heifers.Biol Reprod. 2017 Jul 1;97(1):104-118. doi: 10.1093/biolre/iox061. Biol Reprod. 2017. PMID: 28633489
-
Symposium review: Immunological detection of the bovine conceptus during early pregnancy.J Dairy Sci. 2019 Apr;102(4):3766-3777. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-15668. Epub 2019 Feb 1. J Dairy Sci. 2019. PMID: 30712941 Review.
-
Practical aspects of the fertility of dairy cattle.J Reprod Dev. 2011 Feb;57(1):17-33. doi: 10.1262/jrd.10-197e. J Reprod Dev. 2011. PMID: 21422734 Review.
References
-
- Abdalla H.B., Napimoga M.H., Lopes A.H., de Macedo Maganin A.G., Cunha T.M., Van Dyke T.E., and Clemente Napimoga J.T.. 2020. Activation of PPAR-γ induces macrophage polarization and reduces neutrophil migration mediated by heme oxygenase 1. Int Immunopharmacol 8: 106565. 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106565. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahmadi M.R., Nazifi S., and Ghaisari H.R.. 2006. Comparison of hormonal changes of estrous cycle with cytology of cervical mucosa and hematological parameters in dairy heifers. Comp Clin Path 15:94–97. 10.1007/s00580-006-0613-7. - DOI
-
- De Almeida A.C., Barbosa S.M., De Lourdes Rios Barjas-Castro M., Olalla-Saad S.T., and Condino-Neto A.. 2012. IFN-β, IFN-γ, and TNF-α decrease erythrophagocytosis by human monocytes independent of SIRP-α or SHP-1 expression. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 34:1054–1059. 10.3109/08923973.2012.697470. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
