Clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes of patients with IgG4-positive ocular adnexal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 38767546
- PMCID: PMC11670843
- DOI: 10.4103/IJO.IJO_2560_23
Clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes of patients with IgG4-positive ocular adnexal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
Purpose: To explore the clinicopathological characteristics of immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-positive ocular adnexal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma (OAML) and associated patient treatment outcomes.
Methods: Medical records from patients diagnosed with IgG4-positive OAML treated at the West China Hospital between January 2016 and August 2023 were retrospectively analyzed.
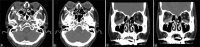
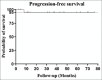
Results: This study included data from 22 patients (11 males, 11 females), aged between 36 and 83 years, with disease durations from 1 month to 30 years. Sixteen cases exhibited unilateral ocular involvement (ten left eyes, six right eyes), while six exhibited bilateral involvement. Common clinical symptoms included ocular masses, eyelid swelling, and proptosis, with the orbit and lacrimal gland being the most commonly impacted sites. Among the 22 patients, 13 who were clinically suspected of having IgG4-related ophthalmic disease (IgG4-ROD) underwent serum IgG4 testing pre-operatively, revealing elevated IgG4 levels in 11 of these patients. The use of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging facilitated the evaluation of the location and size of lesions. All 22 patients received surgical treatment. Subsequently, 14 of these patients underwent local radiotherapy, five received post-operative chemotherapy, and three were closely observed. The follow-up period of patients in this study was 3-77 months, with an average follow-up time of 36 months. Except for one patient who died of disease progression, all others showed favorable prognoses with significant improvements.
Conclusions: These results support the classification of IgG4-positive OAML as a distinct OAML sub-type with clinical features that partially overlap with IgG4-ROD. Therefore, accurate differentiation between OAML and IgG4-ROD is imperative, necessitating timely surgical intervention and precise pathological diagnosis to prevent diagnostic errors and inappropriate treatment. Currently, no standardized treatments for IgG4-positive OAML exist, but our results suggest that standard OAML therapies are generally efficacious.
Copyright © 2024 Copyright: © 2024 Indian Journal of Ophthalmology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
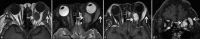

Similar articles
-
Clinical analysis of ocular adnexal mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma with IgG4-related ophthalmic disease.Orbit. 2022 Oct;41(5):551-557. doi: 10.1080/01676830.2021.1962365. Epub 2021 Aug 9. Orbit. 2022. PMID: 34369286
-
Change of Serum IgG4 in Patients with Ocular Adnexal Marginal Zone B Cell Lymphoma Associated with IgG4-Related Ophthalmic Disease After Treatment.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Sep;33(7):543-548. doi: 10.1089/jop.2016.0175. Epub 2017 May 17. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28514197
-
Suggestion of response evaluation criteria in patients with ocular adnexal mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma (OAML).Ann Hematol. 2015 Jul;94(7):1185-93. doi: 10.1007/s00277-015-2339-6. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Ann Hematol. 2015. PMID: 25728714
-
Orbital and ocular adnexal lymphoma: a review of epidemiology and prognostic factors in Taiwan.Eye (Lond). 2021 Jul;35(7):1946-1953. doi: 10.1038/s41433-020-01198-y. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Eye (Lond). 2021. PMID: 32994547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lacrimal gland sparing IgG4-related disease in the orbit.Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2013 Jun;21(3):220-4. doi: 10.3109/09273948.2012.762981. Epub 2013 Mar 12. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2013. PMID: 23480602 Review.
References
-
- Sato Y, Ohshima K, Takata K, Huang X, Cui W, Ohno K, et al. Ocular adnexal IgG4-producing mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma mimicking IgG4-related disease. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2012;52:51–5. - PubMed
-
- Sohn EJ, Ahn HB, Roh MS, Jung WJ, Ryu WY, Kwon YH. Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-positive ocular adnexal mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma and idiopathic orbital inflammation. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2018;34:313–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

