Clinical outcomes of topography-guided versus wavefront-optimized LASIK for correction of myopia and compound myopic astigmatism
- PMID: 38767561
- PMCID: PMC11668192
- DOI: 10.4103/IJO.IJO_2012_23
Clinical outcomes of topography-guided versus wavefront-optimized LASIK for correction of myopia and compound myopic astigmatism
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the safety, efficacy, and visual outcomes of topography-guided (TG) LASIK ablation versus advanced ablation algorithm (AAA) on Zeiss Mel 90 on virgin eyes.
Setting: A tertiary care hospital in north India.
Design: A retrospective comparative study.
Methods: Case sheets of 30 patients who underwent TG LASIK and 45 patients who underwent AAA LASIK between January 2021 and September 2022 were retrieved and reviewed. The TG group included 60 eyes of 30 patients, and the AAA group included age- and sex-matched 90 eyes of 45 patients. Both groups were compared for visual outcomes, residual refraction, and root-mean-square higher-order aberrations (rms HOA) at 1 week, 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months postoperatively and using unpaired t -test and Mann-Whitney U test.
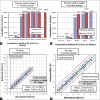
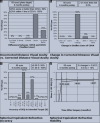
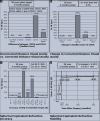
Results: The mean preoperative spherical equivalent in the TG group and AAA group was - 3.12 (1.67) and - 3.19 (1.61), respectively. The safety and efficacy of the treatment were 100% in both groups. The postoperative increase in rms HOA was comparable in both groups ( P = 0.55). The ablation duration was significantly longer in topo-guided LASIK ( P = 0.001).
Conclusion: AAA LASIK on MEL 90 is comparable to topography-guided LASIK for the management of low myopia and myopic astigmatism.
Copyright © 2024 Copyright: © 2024 Indian Journal of Ophthalmology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Randomized Comparative Study of Topography-Guided Versus Wavefront-Optimized FS-LASIK for Correcting Myopia and Myopic Astigmatism.J Refract Surg. 2019 Sep 1;35(9):575-582. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20190819-01. J Refract Surg. 2019. PMID: 31498415 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of outcomes after topography-modified refraction versus wavefront-optimized versus manifest topography-guided LASIK.BMC Ophthalmol. 2020 May 14;20(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s12886-020-01459-0. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32410588 Free PMC article.
-
Topography-guided versus wavefront-optimized laser in situ keratomileusis for myopia: Surgical outcomes.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2019 Jul;45(7):959-965. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2019.01.031. Epub 2019 Jun 10. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2019. PMID: 31196580
-
Topography-Guided LASIK Versus Small Incision Lenticule Extraction (SMILE) for Myopia and Myopic Astigmatism: A Randomized, Prospective, Contralateral Eye Study.J Refract Surg. 2017 May 1;33(5):306-312. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20170221-01. J Refract Surg. 2017. PMID: 28486721 Clinical Trial.
-
Wavefront excimer laser refractive surgery for adults with refractive errors.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Dec 18;12(12):CD012687. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012687.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33336797 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mrochen M, Donitzky C, Wüllner C, Löffler J. Wavefront-optimized ablation profiles: Theoretical background. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004;30:775–85. - PubMed
-
- Knorz MC, Jendritza B. Topographically-guided laser in situ keratomileusis to treat corneal irregularities. Ophthalmology. 2000;107:1138–43. - PubMed
-
- Tan J, Simon D, Mrochen M, Por YM. Clinical results of topography-based customized ablations for myopia and myopic astigmatism. J Refract Surg Thorofare NJ 1995. 2012;28:S829–36. - PubMed
-
- Dougherty PJ, Waring G, Chayet A, Fischer J, Fant B, Bains HS. Topographically guided laser in situ keratomileusis for myopia using a customized aspherical treatment zone. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008;34:1862–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

